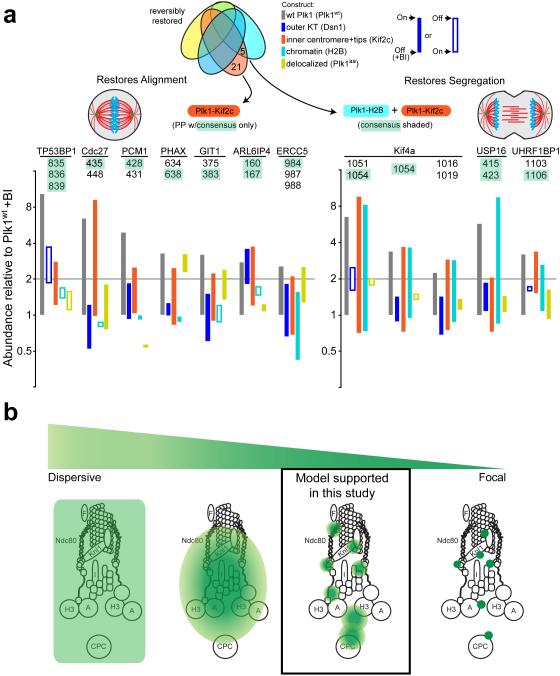
Figure 6. Functional/proteomic signatures and a model for Plk1 activity in the kinetochore.
(a) Phosphopeptides that are restored by constructs concordant with phenotypic rescue of chromosome alignment (left) and accurate chromosome segregation (right). Phosphopeptides (PPs) containing minimal Plk1 consensus are illustrated for each phenotype with bars illustrating difference between +/− BI-2536 for each construct. Left, phosphopeptides that are restored by Plk1wt and Kif2c only. Right, phosphopeptides that are restored with both H2B and Kif2c. (b) A model of Plk1 operation within the kinetochore could range from a highly dispersive operation where one binding partner provides access to all substrates (extreme left), versus focal operation, where Plk1 binds each substrate directly (extreme right). Our data support an intermediate model where Plk1 at each subcompartment can access elicit ~40 phosphorylation events, with minimal overlap between inner centromere, chromatin, and the outer kinetochore.