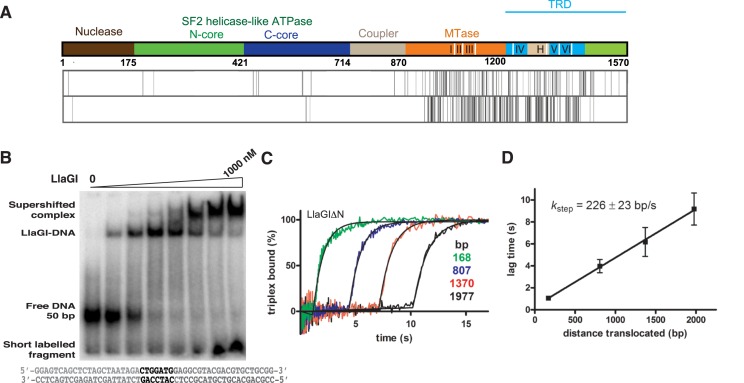
Figure 2.
(A) The domain organization of LlaGI. The positions of the structural elements that recognize the targets are shown as white lines. The amino acid sequence of LlaGI and LlaBIII were aligned pairwise to identify regions of homology, similarity and difference (4). The vertical lines show positions that have amino acid substitutions that are similar (upper row) or different (lower row)—all other positions are identical. (B) EMSA assays of LlaGI binding to 10 nM of a 50 bp DNA substrate with 0, 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, 500 and 1000 nM protein. (C) Triplex displacement reactions on linear DNA. Triplex DNA (with different spacing between the LlaGI site and fluorescent triplex) were pre-incubated with enzyme and the reactions initiated with ATP, to give a final concentration of 1 nM DNA, 100 nM LlaGIΔN and 4 mM ATP at 25°C. The triplex displacement profiles, which have lag phases characteristic of a translocating motor protein, were fitted to Equation (1) to obtain the lag time (Tapp). (D) The linear relationship between Tapp and d was used to estimate the translocation rate. The points are the mean and SD for repeat reactions measured using two different preparations of LlaGIΔN.