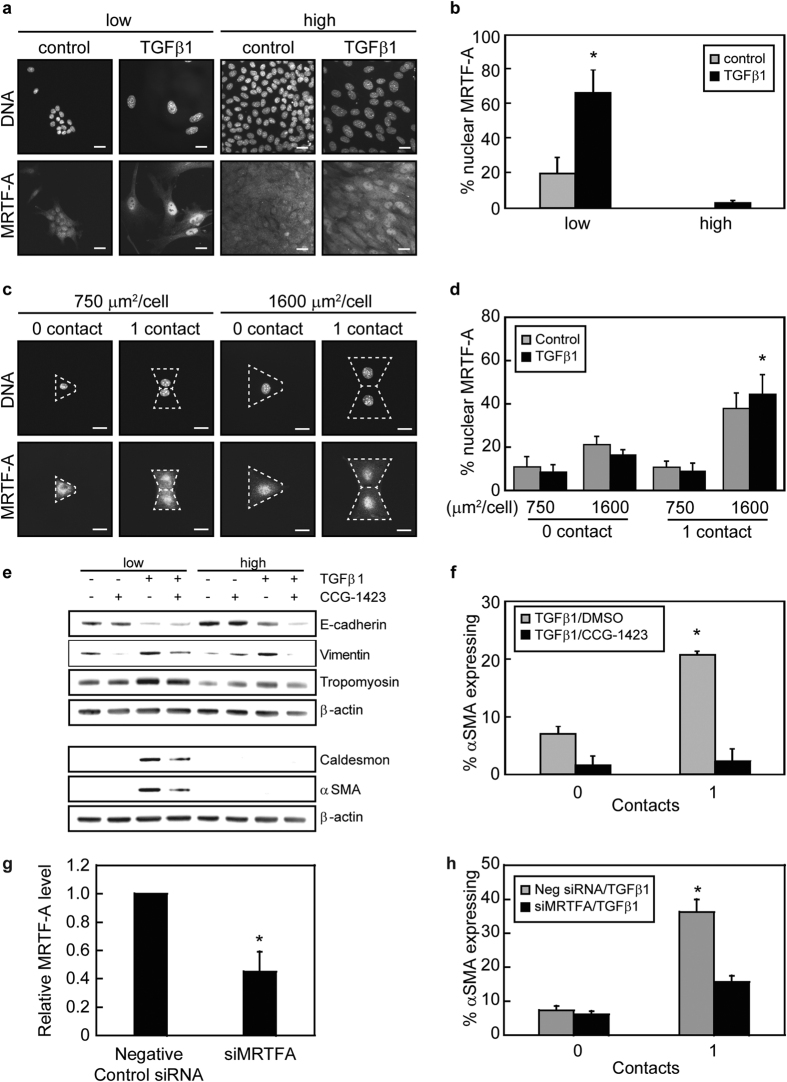
Figure 6. Cell-cell contact and cell-matrix adhesion together regulate αSMA expression by controlling MRTF-A subcellular localization.
(a) Fluorescence microscopy images of MRTF-A localization in cells seeded at low and high densities with and without TGFβ1. Scale bars: 20 μm. (b) Quantification of the percentage of cells with nuclear MRTF-A as a function of cell seeding density. *p < 0.05 compared to all samples. (c) Fluorescence microscopy images of MRTF-A localization in TGFβ1-treated cells cultured on micropatterned triangular and bowtie shaped islands. Dotted white lines outline an individual cell. Scale bars: 20 μm. (d) Quantification of the percentage of cells with nuclear MRTF-A as a function of cell spread area and number of neighboring cells. *p < 0.05 compared to 1600 μm2, 0 contact, TGFβ1. (e) Western blot analysis of EMT markers for NMuMG cells seeded at low (5,000 cells/cm2) and high (100,000 cells/cm2) densities with and without TGFβ1 and DMSO control vehicle or CCG-1423. (f) Percentage of NMuMG cells with a cell spread area of 1600 μm2 expressing αSMA on triangular (0 contact) and bowtie (1 contact) islands following treatment with TGFβ1 and DMSO control vehicle or CCG-1423. *p < 0.05 compared to all samples. (g) Transcript levels of MRTF-A for cells transfected with siRNA. *p < 0.05 compared to negative control siRNA. (h) Percentage of NMuMG cells transfected with siRNA targeting MRTF-A with a cell spread area of 1600 μm2 expressing αSMA on triangular (0 contact) and bowtie (1 contact) islands following treatment with TGFβ1. *p < 0.05 compared to all samples.