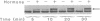Abstract
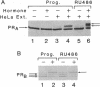
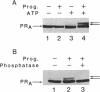
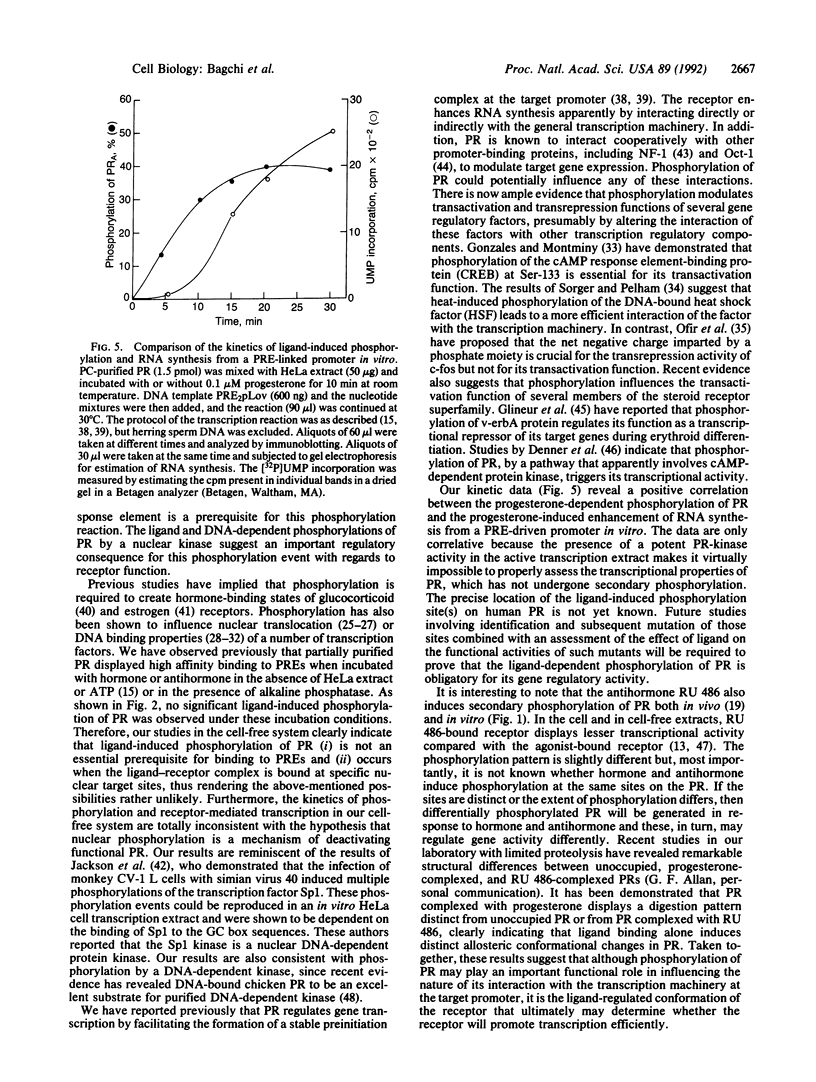
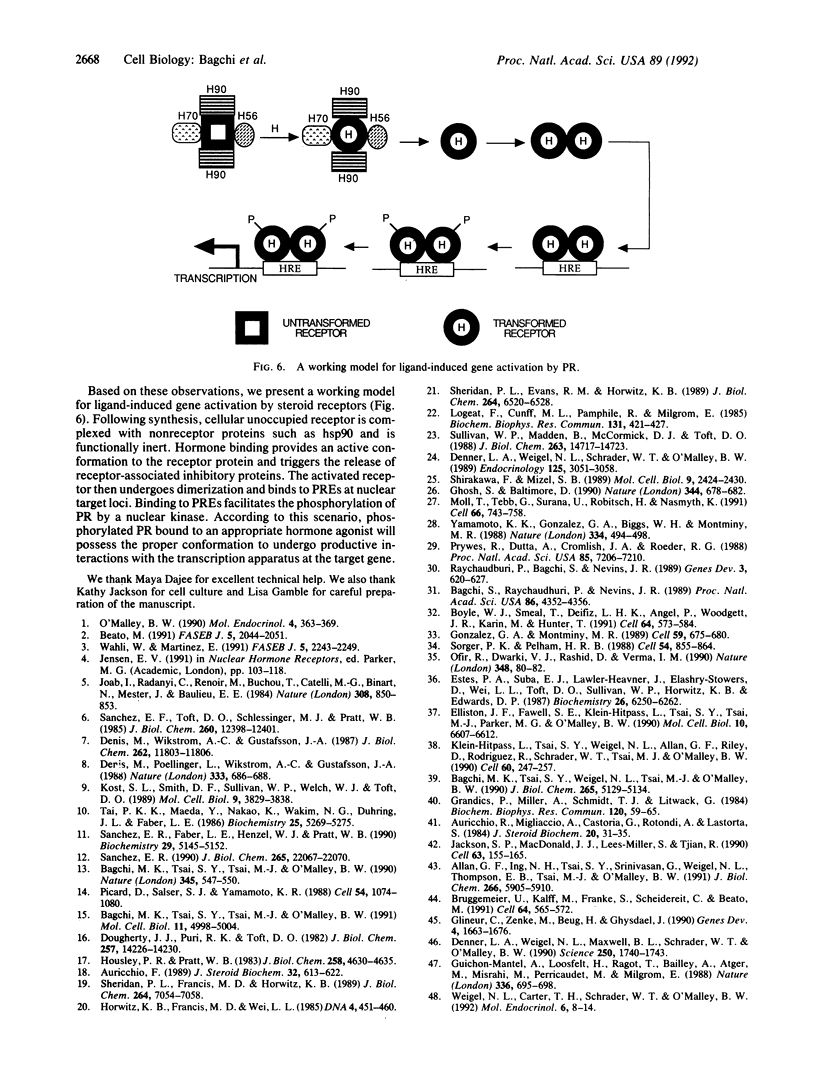
The progesterone receptor (PR), like other members of the steroid receptor family, is a ligand-induced transcription factor. We have demonstrated previously that progesterone-induced binding of PR to a progesterone response element (PRE)-linked promoter stimulates RNA synthesis from that promoter in a cell-free transcription extract. It has been established that a hormone-mediated activation of PR beyond the removal of associated heat shock proteins is essential for efficient transactivation of the target gene. We now report that treatment with hormone leads rapidly to multiple phosphorylations of both the A and B forms of human PR in a HeLa nuclear extract. The putative kinase is present in the transcriptional extract but fails to phosphorylate the receptor significantly in the absence of specific hormone or DNA. Efficient phosphorylation of the PR occurs only in the presence of PREs, indicating that ligand-induced binding of PR to its cognate DNA response element makes it a preferred substrate for the kinase. The kinetics of the phosphorylation reaction overlap the kinetics of hormone-dependent RNA synthesis from a PRE-containing target promoter in vitro. We postulate that ligand and DNA-dependent phosphorylation of PR is an important functional event in the process leading to receptor-mediated transactivation of target genes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan G. F., Ing N. H., Tsai S. Y., Srinivasan G., Weigel N. L., Thompson E. B., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Synergism between steroid response and promoter elements during cell-free transcription. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5905–5910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auricchio F., Migliaccio A., Castoria G., Rotondi A., Lastoria S. Direct evidence of in vitro phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of the estradiol-17 beta receptor. Role of Ca2+-calmodulin in the activation of hormone binding sites. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Jan;20(1):31–35. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auricchio F. Phosphorylation of steroid receptors. J Steroid Biochem. 1989 Apr;32(4):613–622. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(89)90397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Identification of a functional intermediate in receptor activation in progesterone-dependent cell-free transcription. Nature. 1990 Jun 7;345(6275):547–550. doi: 10.1038/345547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Progesterone enhances target gene transcription by receptor free of heat shock proteins hsp90, hsp56, and hsp70. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4998–5004. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi M. K., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Regulation of in vitro transcription by progesterone receptor. Characterization and kinetic studies. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5129–5134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi S., Raychaudhuri P., Nevins J. R. Phosphorylation-dependent activation of the adenovirus-inducible E2F transcription factor in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(12):4352–4356. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.12.4352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Transcriptional control by nuclear receptors. FASEB J. 1991 Apr;5(7):2044–2051. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.7.2010057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Smeal T., Defize L. H., Angel P., Woodgett J. R., Karin M., Hunter T. Activation of protein kinase C decreases phosphorylation of c-Jun at sites that negatively regulate its DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):573–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90241-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Poellinger L., Wikstöm A. C., Gustafsson J. A. Requirement of hormone for thermal conversion of the glucocorticoid receptor to a DNA-binding state. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):686–688. doi: 10.1038/333686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Wikström A. C., Gustafsson J. A. The molybdate-stabilized nonactivated glucocorticoid receptor contains a dimer of Mr 90,000 non-hormone-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11803–11806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denner L. A., Weigel N. L., Maxwell B. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Regulation of progesterone receptor-mediated transcription by phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1740–1743. doi: 10.1126/science.2176746. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denner L. A., Weigel N. L., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Hormone-dependent regulation of chicken progesterone receptor deoxyribonucleic acid binding and phosphorylation. Endocrinology. 1989 Dec;125(6):3051–3058. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-6-3051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dougherty J. J., Puri R. K., Toft D. O. Phosphorylation in vivo of chicken oviduct progesterone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14226–14230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliston J. F., Fawell S. E., Klein-Hitpass L., Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., Parker M. G., O'Malley B. W. Mechanism of estrogen receptor-dependent transcription in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6607–6612. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estes P. A., Suba E. J., Lawler-Heavner J., Elashry-Stowers D., Wei L. L., Toft D. O., Sullivan W. P., Horwitz K. B., Edwards D. P. Immunologic analysis of human breast cancer progesterone receptors. 1. Immunoaffinity purification of transformed receptors and production of monoclonal antibodies. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 22;26(19):6250–6262. doi: 10.1021/bi00393a045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Activation in vitro of NF-kappa B by phosphorylation of its inhibitor I kappa B. Nature. 1990 Apr 12;344(6267):678–682. doi: 10.1038/344678a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glineur C., Zenke M., Beug H., Ghysdael J. Phosphorylation of the v-erbA protein is required for its function as an oncogene. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1663–1676. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez G. A., Montminy M. R. Cyclic AMP stimulates somatostatin gene transcription by phosphorylation of CREB at serine 133. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):675–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandics P., Miller A., Schmidt T. J., Litwack G. Phosphorylation in vivo of rat hepatic glucocorticoid receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Apr 16;120(1):59–65. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiochon-Mantel A., Loosfelt H., Ragot T., Bailly A., Atger M., Misrahi M., Perricaudet M., Milgrom E. Receptors bound to antiprogestin from abortive complexes with hormone responsive elements. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):695–698. doi: 10.1038/336695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Francis M. D., Wei L. L. Hormone-dependent covalent modification and processing of human progesterone receptors in the nucleus. DNA. 1985 Dec;4(6):451–460. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housley P. R., Pratt W. B. Direct demonstration of glucocorticoid receptor phosphorylation by intact L-cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4630–4635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., MacDonald J. J., Lees-Miller S., Tjian R. GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90296-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joab I., Radanyi C., Renoir M., Buchou T., Catelli M. G., Binart N., Mester J., Baulieu E. E. Common non-hormone binding component in non-transformed chick oviduct receptors of four steroid hormones. 1984 Apr 26-May 2Nature. 308(5962):850–853. doi: 10.1038/308850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Allan G. F., Riley D., Rodriguez R., Schrader W. T., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. The progesterone receptor stimulates cell-free transcription by enhancing the formation of a stable preinitiation complex. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):247–257. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90740-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kost S. L., Smith D. F., Sullivan W. P., Welch W. J., Toft D. O. Binding of heat shock proteins to the avian progesterone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3829–3838. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Le Cunff M., Pamphile R., Milgrom E. The nuclear-bound form of the progesterone receptor is generated through a hormone-dependent phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):421–427. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91819-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll T., Tebb G., Surana U., Robitsch H., Nasmyth K. The role of phosphorylation and the CDC28 protein kinase in cell cycle-regulated nuclear import of the S. cerevisiae transcription factor SWI5. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):743–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90118-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley B. The steroid receptor superfamily: more excitement predicted for the future. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Mar;4(3):363–369. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-3-363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ofir R., Dwarki V. J., Rashid D., Verma I. M. Phosphorylation of the C terminus of Fos protein is required for transcriptional transrepression of the c-fos promoter. Nature. 1990 Nov 1;348(6296):80–82. doi: 10.1038/348080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Dutta A., Cromlish J. A., Roeder R. G. Phosphorylation of serum response factor, a factor that binds to the serum response element of the c-FOS enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7206–7210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raychaudhuri P., Bagchi S., Nevins J. R. DNA-binding activity of the adenovirus-induced E4F transcription factor is regulated by phosphorylation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):620–627. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Faber L. E., Henzel W. J., Pratt W. B. The 56-59-kilodalton protein identified in untransformed steroid receptor complexes is a unique protein that exists in cytosol in a complex with both the 70- and 90-kilodalton heat shock proteins. Biochemistry. 1990 May 29;29(21):5145–5152. doi: 10.1021/bi00473a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R. Hsp56: a novel heat shock protein associated with untransformed steroid receptor complexes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22067–22070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Toft D. O., Schlesinger M. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the 90-kDa phosphoprotein associated with the untransformed L-cell glucocorticoid receptor is a murine heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12398–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan P. L., Evans R. M., Horwitz K. B. Phosphotryptic peptide analysis of human progesterone receptor. New phosphorylated sites formed in nuclei after hormone treatment. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6520–6528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheridan P. L., Francis M. D., Horwitz K. B. Synthesis of human progesterone receptors in T47D cells. Nascent A- and B-receptors are active without a phosphorylation-dependent post-translational maturation step. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7054–7058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirakawa F., Mizel S. B. In vitro activation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappa B catalyzed by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2424–2430. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan W. P., Madden B. J., McCormick D. J., Toft D. O. Hormone-dependent phosphorylation of the avian progesterone receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14717–14723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai P. K., Maeda Y., Nakao K., Wakim N. G., Duhring J. L., Faber L. E. A 59-kilodalton protein associated with progestin, estrogen, androgen, and glucocorticoid receptors. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):5269–5275. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Martinez E. Superfamily of steroid nuclear receptors: positive and negative regulators of gene expression. FASEB J. 1991 Jun;5(9):2243–2249. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.9.1860615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel N. L., Carter T. H., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. Chicken progesterone receptor is phosphorylated by a DNA-dependent protein kinase during in vitro transcription assays. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Jan;6(1):8–14. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.1.1738374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]