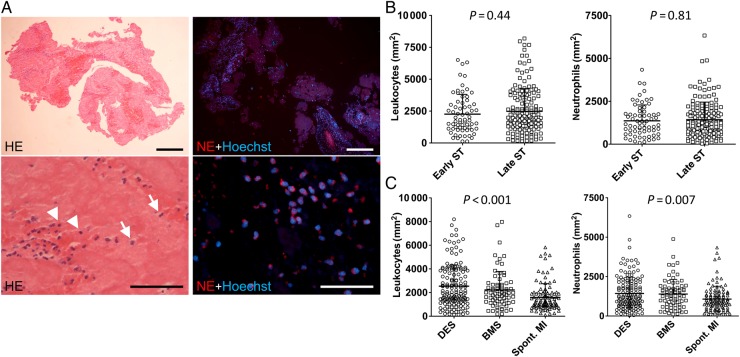
Figure 3.
Leukocyte accumulation in stent thrombus specimens. (A) Leukocyte accumulation in human stent thrombus specimens. Left images: Haematoxylin–eosin staining (n = 253). Arrows indicate granulocytes, arrowheads indicate mononuclear cells. Right images: immunofluorescence staining of neutrophil elastase to identify neutrophils (n = 229). Nuclei are counterstained with Hoechst. Bars, 200 µm (upper row) and 50 µm (bottom row); (B) Quantification of leukocytes and neutrophils in early (n = 67) vs. late (n = 162) stent thrombosis (leukocytes: P = 0.44; neutrophils: P = 0.81); (C) Leukocytes and neutrophils in stent thrombosis from drug-eluting stents (n = 149) and bare metal stents (n = 73) and in thrombi aspirated from patients with spontaneous myocardial infarction (spont. myocardial infarction; n = 104) (P < 0.05 for drug-eluting stents vs. spont. myocardial infarction and bare metal stents vs. spont. myocardial infarction). Shown are mean + SD, each symbol in (B) and (C) represents one individual patient.