Fig. 2.
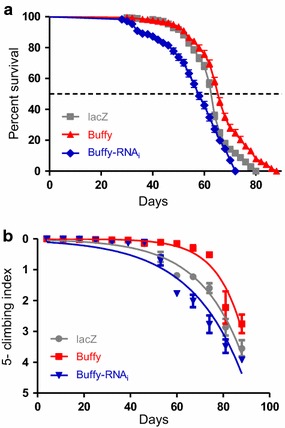
Buffy alters lifespan and climbing ability when mis-expressed in DA neurons. a Directed expression of UAS-Buffy in the DA neurons driven by Ddc-Gal4 results in increased survival compared to the controls overexpressing UAS-lacZ, while inhibition via Buffy-RNAi results in reduced survival. The genotypes are UAS-lacZ/Ddc-Gal4; UAS-Buffy/Ddc-Gal4; and UAS-Buffy-RNAi/Ddc-Gal4. Longevity is shown as percent survival (P < 0.01, determined by log-rank and n ≥ 200). b Directed expression of UAS-Buffy results in increased climbing ability as determined by non-linear fitting of the climbing curves and comparing at 95 % confidence intervals. Inhibition by Buffy-RNAi decreased the locomotor ability when expressed in dopaminergic neurons. The genotypes are UAS-lacZ/Ddc-Gal4; UAS-Buffy/Ddc-Gal4; and UAS-Buffy-RNAi/Ddc-Gal4. Error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM), asterisks represents statistically significant result and n = 50
