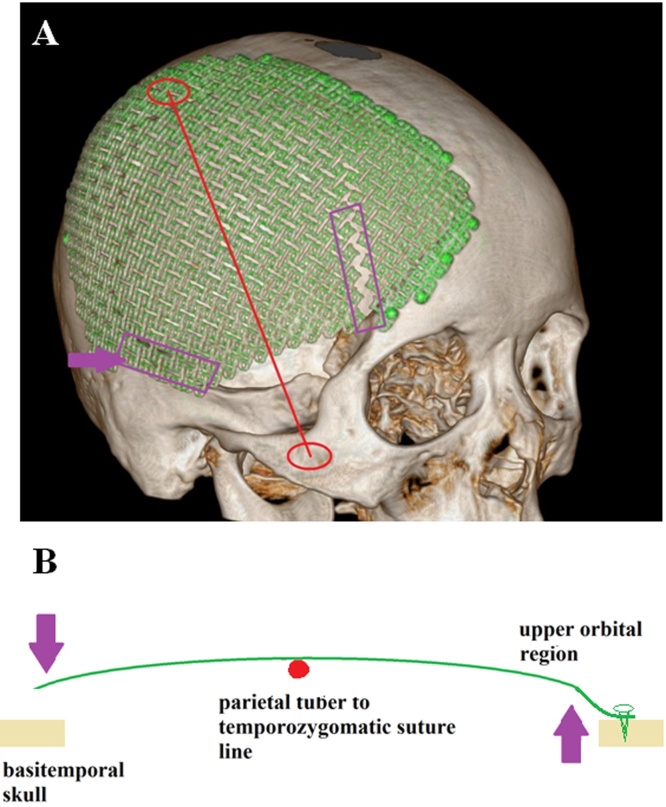
Fig. 4.
(A and B) A force analysis model of the skull when it was lying on its lateral side on a horizontal plate. On the skull lateral side, the parietal tuber (PT) and temporozygomatic suture (TS) were two most prominent spots, which made every single dot on the PT-TS line serve as a fulcrum. Because the prosthesis was not anchored to the basitemporal skull, the micro gap between prosthesis and skull due to head-pillow contact generated a dynamic load to the prosthesis. Thus, via the PT-TS line, this inward dynamic load at basitemporal locus generated an outward force at proximal pterion point region on the titanium mesh, which led to a fatigue effect and eventually sheared the titanium mesh.