Figure 2.
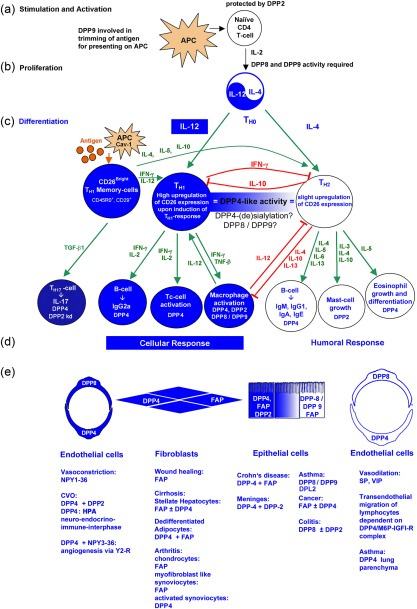
Involvement of dipeptidyl peptidase (DP)4‐like enzymes in T cell effector response. (a) Naive CD4 T cells are protected by DP2. Antigen‐presenting cells (APC) stimulate and activate naive CD4 T cells. (b) Secretion of interleukin (IL)‐2 results in clonal expansion, yielding T helper type 0 (Th0) cells. Enzymatic activities of DP8 and DP9 are required for this process. (c) Secretion of IL‐12 and IL‐4 results in the differentiation of Th1 and Th2 effector cells, respectively. Differentiation into Th1 cells initiates the up‐regulation of DP4 expression. A small subset of CD26bright memory T cells already expresses high amounts of CD26. Upon antigen stimulation, CD26bright memory T cells augment the Th1 and Th2 response by secreting interferon (IFN)‐γ, IL‐12, IL‐4, IL‐5 and IL‐10, respectively. Differentiation into Th2 cells results in only a slight up‐regulation of CD26. The DP4 activity is equal in both T effector cells, due probably to specific DP4 isoforms or DP8 and/or DP9. (d) Differentiated T effector cells secrete specific cytokines that induce differentiation of leucocytes, resulting in cellular response by Th1 and humoral by Th2 effector cells. Leucocytes expressing DP4, DP2 or DP8/9 are indicated. Green arrow = stimulation; red arrow = suppression. 16, 17, 28, 31, 39, 40, 41, 77, 78, 79, 80, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 102, 104.
