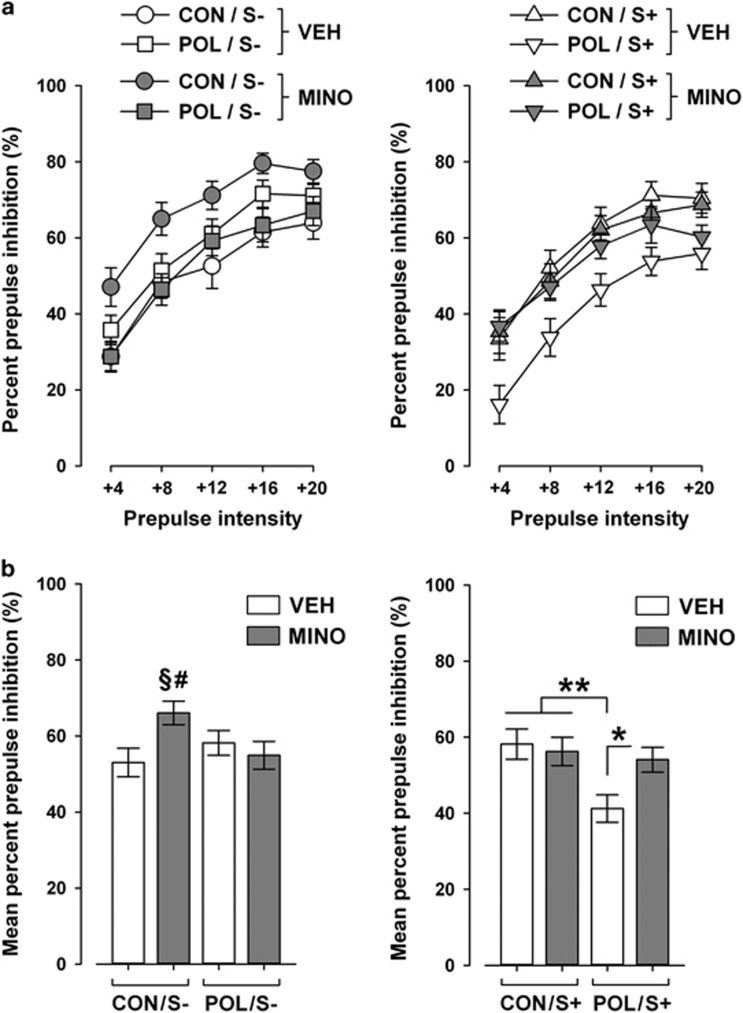
Figure 2.
Prepulse inhibition of the acoustic startle reflex in adult offspring exposed to single or combined prenatal immune activation and peripubertal stress with or without preventive minocycline (MINO) treatment. Pregnant mice were injected with 1 mg kg−1 poly(I:C) (POL) or physiological saline (control (CON)), and the resulting offspring were subjected to sub-chronic stress (S+) or left undisturbed (S−) during peripubertal maturation. During the stress procedure, half of the animals received MINO treatment (30 mg kg−1 per day, per os in drinking water), and the other half vehicle (VEH; = regular tap water) treatment. (a) The line plots depict percent prepulse inhibition as a function of increasing prepulse intensities (dB above background of 65 dB). (b) The bar plots show the mean percent prepulse inhibition across all five prepulse intensities. §P<0.01, reflecting the significant difference between CON/S−/MINO offspring and CON/S−/VEH offspring; #P<0.05, reflecting the significant difference between CON/S−/MINO offspring and POL/S−/MINO offspring; *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, reflecting the indicated differences in the S+ groups. N=12–18 per group. All data are means±s.e.m.