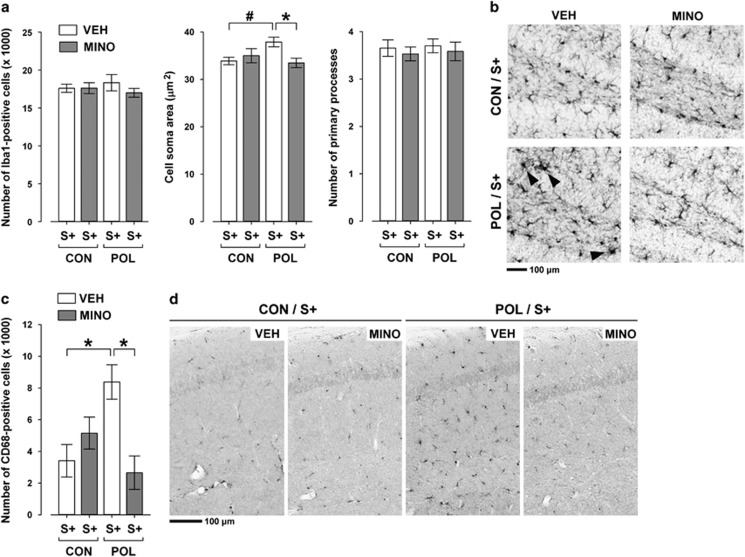
Figure 4.
Effects of minocycline (MINO) on microglia abnormalities in the hippocampus of stressed offspring born to control or gestationally immune-challenged mothers. Pregnant mice were injected with 1 mg kg−1 poly(I:C) (POL) or physiological saline (control (CON)), and the resulting offspring were subjected to sub-chronic stress (S+) during peripubertal maturation. During the stress procedure, half of the animals received MINO treatment (30 mg kg−1 per day, per os in drinking water), and the other half vehicle (VEH; = regular tap water) treatment. (a) The bar plots depict the stereological estimates of Iba1-positive cells, as well as cell soma area and number of primary processes of Iba1-positive microglia. *P<0.05 and #P=0.07; N=5 per group. (b) The photomicrographs show representative sections stained with anti-Iba1 antibody. Note the enlargement of the cell soma area in Iba1-positive microglia cells in VEH-treated POL/S+ offspring relative to the other groups (indicated by the black arrow head). (c) The bar plot shows the stereological estimates of activated CD68-positive microglia cells. *P<0.05, N=5 per group. (d) The photomicrographs show representative coronal brain sections stained with anti-CD68 antibody. Note the increase in microglial CD68 expression in VEH-treated POL/S+ offspring relative to the other groups. All data are means±s.e.m.