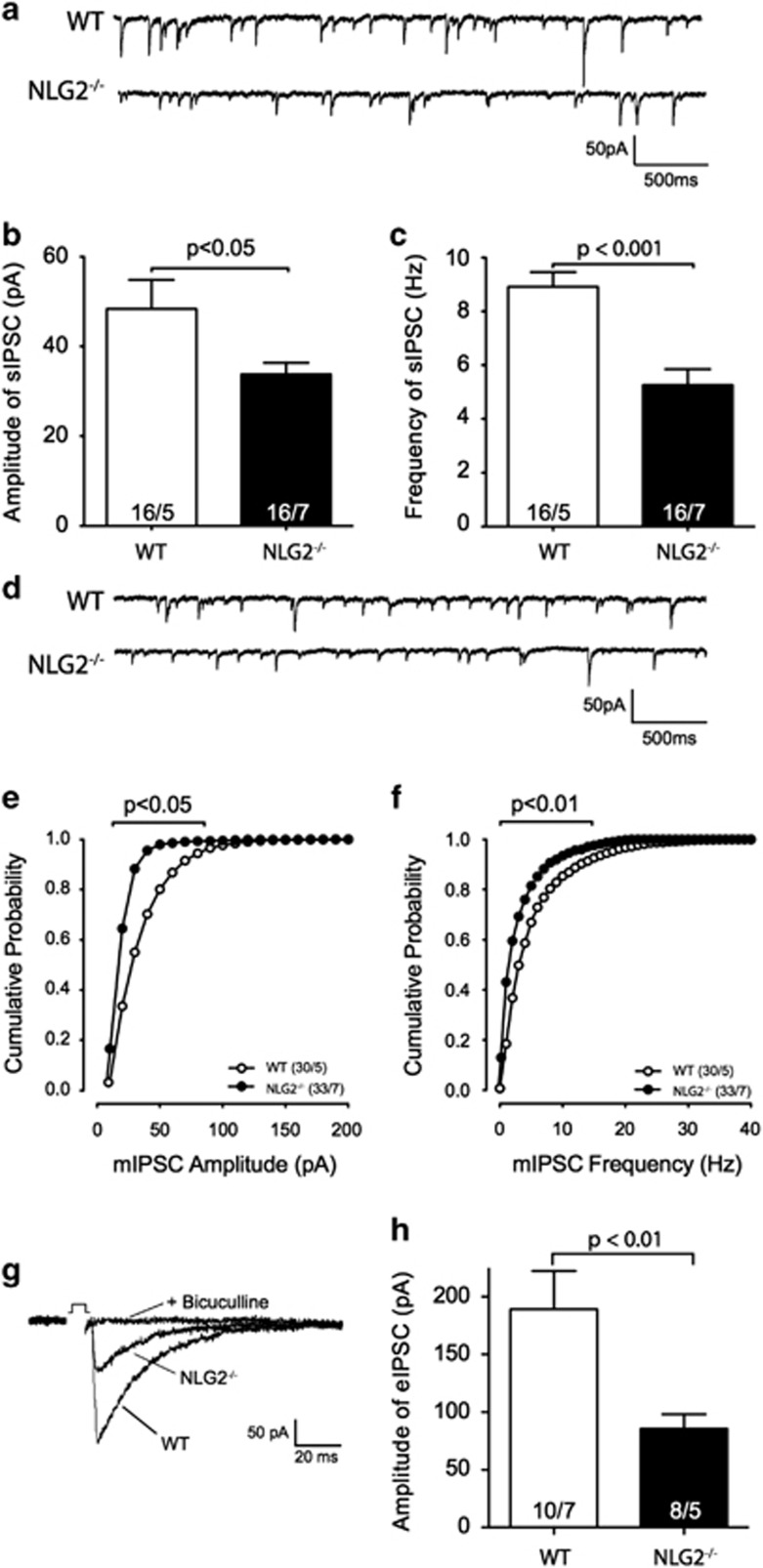
Figure 5.
Deletion of Nlgn2 attenuates the overall inhibitory inputs to PrL, especially the synaptic inhibition from IL to PrL. (a–c) Sample traces (a), averaged amplitude (b) and averaged frequency (c) of spontaneous IPSCs in pyramidal neurons of PrL; (d–f) Sample traces (d), cumulative probability of amplitude (e) and frequency (f) of miniature IPSCs in pyramidal neurons of PrL; (g and h) Sample traces (g) and average amplitudes (h) of IPSCs in layer II/III pyramidal neurons of PrL evoked by stimulation in IL in wild-type (WT) and Nlgn2−/− mice. Note that the numbers within the bar diagrams n/N indicate the number of cells (n) tested/number of mice (N). IL, infralimbic cortex; IPSC, inhibitory postsynaptic current; PrL, prelimbic cortex.