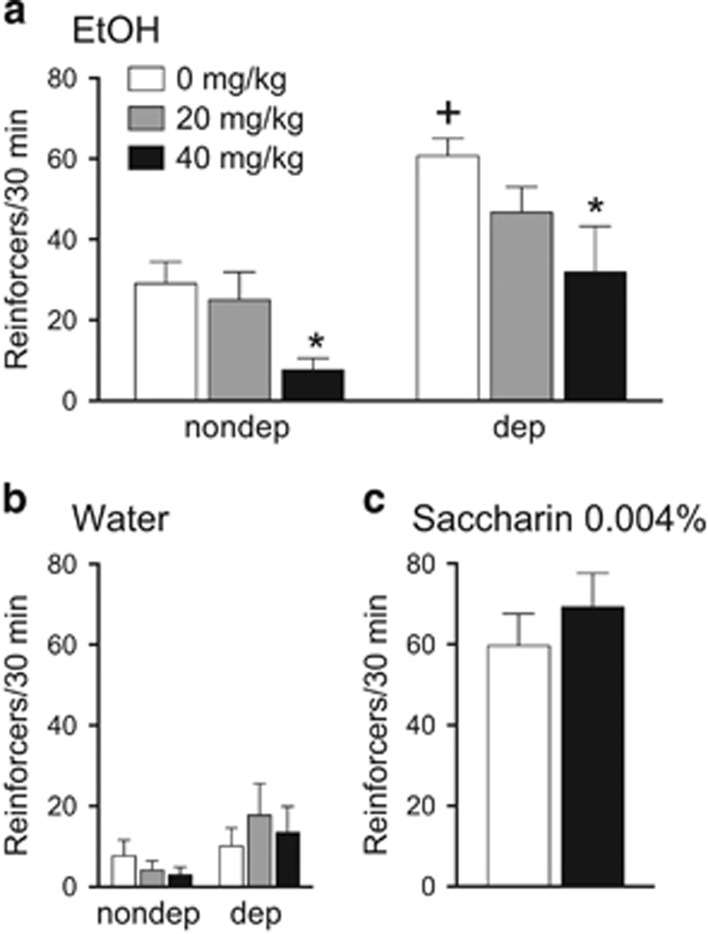
Figure 1.
CBX reduces ethanol intake in rats in an operant self-administration paradigm. (a) Acute, systemic administration of CBX decreases operant alcohol self-administration both in dependent (dep) and nondependent (nondep) rats. (b) CBX did not influence water intake in any group. (c) Acute, systemic administration of CBX does not affect operant self-administration of saccharin-sweetened water. Rats were given CBX (0, 20 and 40 mg kg−1 or 0 and 40 mg kg−1; intraperitoneally) 90 min before alcohol (10%, w/v), water or saccharin (0.004%) self-administration (30 min session; fixed-ratio 1). The data represent means and s.e.m. *P<0.05, significant difference from respective vehicle; +P<0.05, significant difference from vehicle (saline)-treated nondependent rats. N=9–10 per group.