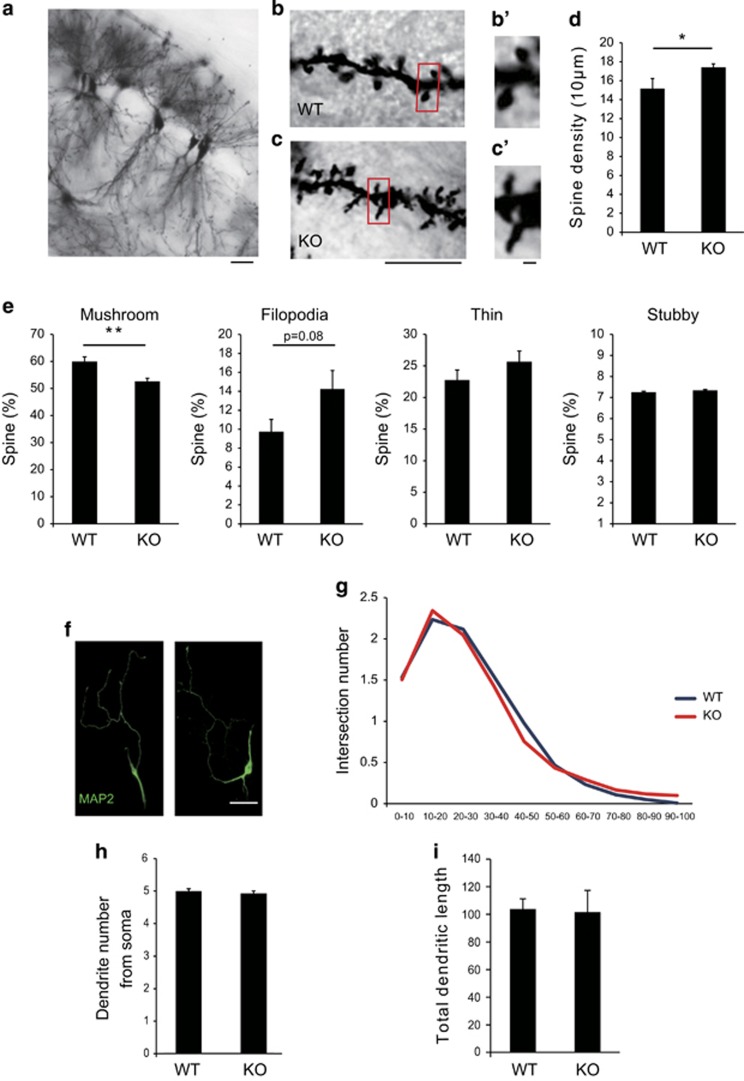
Figure 3.
Structural analysis of dendrites and spines of hippocampal CA1 of JMJD2B mutant mice.(a) Representative Golgi staining image in the hippocampal CA1 region. (b and c) Representative Golgi staining images of dendritic spines in the hippocampal CA1 region in each genotype. (b′ and c′) Magnified images of b and c. (d) The total spine numbers in the CA1 region of the two genotypes. (e) The percentage of mature mushroom, filopodia, thin and stubby-type spines of CA1 pyramidal neurons. *P<0.05; **P<0.01. WT: n=6, KO: n=5 (a–e). Error bars represent s.e.m. (f; left) Representative images of hippocampal neurons cultured for 7 days, and stained with MAP2. (g) Sholl analysis of hippocampal neurons of each genotype. A concentric circle was drawn every 10 μm from a central focus on the neuronal soma and the number of intersections were counted. NS, not significant. (WT, KO: n=4). (h) The number of dendrites extending from the soma. (WT, KO: n=3). (i) Total dendritic length measured from the soma of cultured hippocampal neurons. Total dendritic length measured from the soma of cultured hippocampal neurons. (WT, KO: n=4). WT, wild-type mice; KO, JMJD2B mutant mice. Scale bars: (a) 10 μm, (b and c) 10 μm, (b'and c') 1 μm, (f) 20 μm. Error bars represent s.e.m. (d, e, h, i).