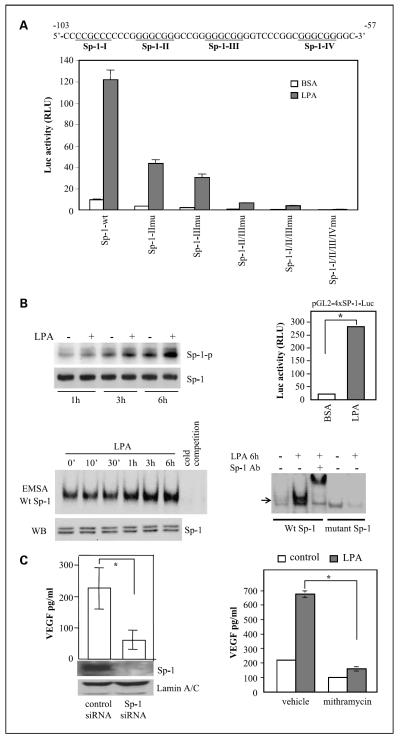
Fig. 6.
Requirement of the Sp-1 transcription factor for activation of the VEGF promoter and VEGF production. A, Sp-1 sites were essential for LPA-dependent activation of the VEGF promoter. The DNA sequences listed are the VEGF promoter region spanning the four potential Sp-1 sites (underlined). Caov-3 cells were transfected with wild-type pGL2-VEGF123-Luc or Sp-1 mutant vectors. Luciferase activities from wild-type or mutant vectors induced by LPA (10 μmol/L, 6 h). B, LPA-stimulated Sp-1 phosphorylation and Sp-1 DNA-binding and transcriptional activities. Caov-3 cells were starved for 16 h, incubated with phosphate-free DMEM for 20 min, and then labeled with 32P in phosphate-free DMEM for 3 h before incubation with LPA (10 μmol/L) or vehicle (BSA) for 1, 3, or 6 h. Sp-1 was immunoprecipitated from cell lysates, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and transferred to Immun-Blot membrane for autoradiograph followed by immunoblotting for Sp-1 protein (left, top). Sp-1 DNA-binding activity was assessed by electrophoretic mobility shift assay (bottom). Nuclear extracts of Caov-3 cells stimulated for the indicated periods with LPA (10 μmol/L) were incubated with 32P-labeled Sp-1 consensus oligonucleotides (Wt Sp-1) or the inactive mutant form (mutant Sp-1). Reaction mixes were run on 5% native polyacrylamide gels and autoradiographed. The Sp-1 protein levels in nuclear extracts were examined by immunoblotting (left, bottom).The specificity of binding to the 32P-labeled Sp-1 probe was confirmed by inhibition of the binding with the unlabeled oligonucleotide (cold competition; left, bottom) and by a supershift assay with a Sp-1-specific antibody (Sp-1 Ab; right, bottom). LPA-induced Sp-1 transcriptional activity was analyzed by transfection of Caov-3 cells with the Sp-1 reporter pGL2-4×Sp1-TK-Luc. The cells were stimulated with LPA (10 μmol/L, 6 h) before measuring luciferase activity (right, top). C, Sp-1 was necessary for LPA-induced VEGF production. Caov-3 cells treated with the Sp-1 siRNA or nontarget control siRNA were starved and stimulated with LPA (10 μmol/L) for 16 h before ELISA analysis of VEGF present in culture supernatants. Net increases in VEGF production induced by LPA were calculated by subtracting background VEGF levels in unstimulated cells from LPA-induced VEGF production (left). Right, Caov-3 cells were starved and treated with LPA or vehicle for 16 h in the presence or absence of the Sp-1 inhibitor mithramycin (150 nmol/L).