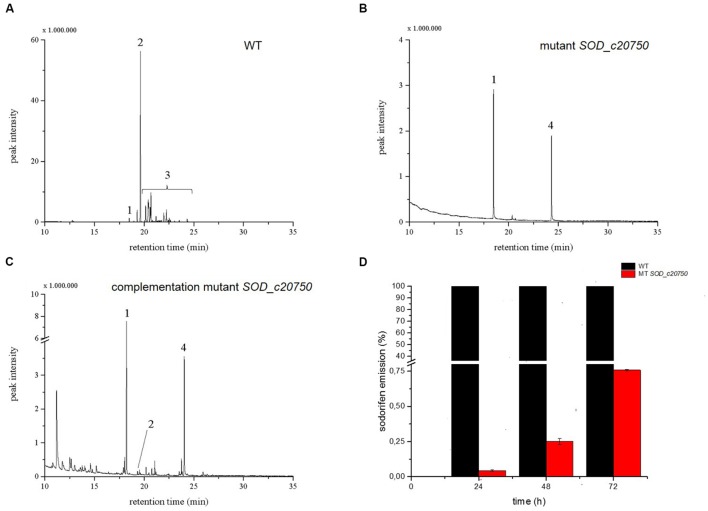
FIGURE 4.
Analysis of the SOD_c20750 (terpene cyclase) knockout and complemented mutant of Serratia plymuthica 4Rx13. Typical volatile organic compound (VOC) profiles of the headspaces of the wild type (A), the SOD_c20750 mutant (B) and the complemented mutant (C) grown in complex medium (NB) in a VOC collection system. VOCs were trapped in the time interval 24–48 h. The compounds were analyzed by GCMS and identified by comparing their mass spectra with those of the Nist107 library. (#1) nonyl acetate was internal standard (peak corresponds to 5 ng), (#2) sodorifen, (#3) sodorifen isomers, (#4) new compound. (D) The emission of the complemented SOD_c20750 mutant (red) at different time points is plotted against the wild type (black), wild type equals 100%. (100% equals 274 ng of sodorifen emission or 12.21 ag sodorifen emission/cell). The peak intensity in the complemented mutant equals 0.70 ng sodorifen emission (=0.03 ag/cell). The knockout mutant did not emit sodorifen and was omitted from the graphic presentation. Error bars indicate min/max values of two clones of one complementation experiment. The emission of sodorifen was restored by introducing a recombinant plasmid consisting of the plasmid pUC19, the wild type gene SOD_c20750 and the 500 bp upstream region of the SOD_c20780 gene.