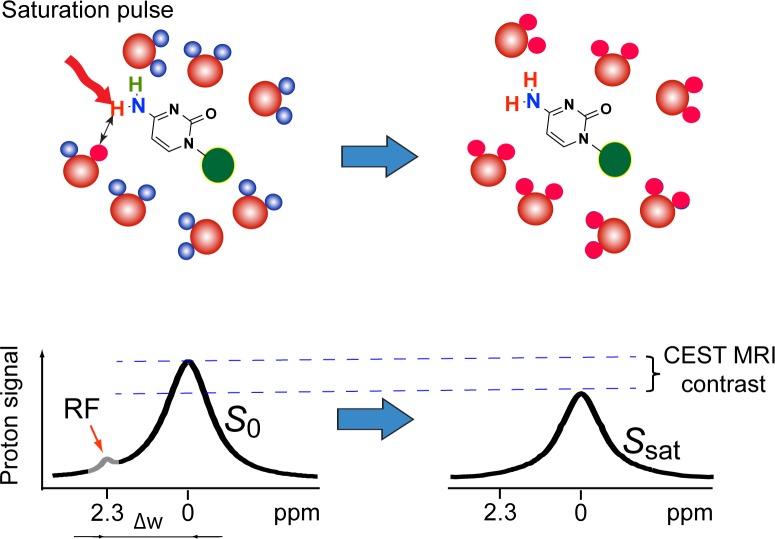
Figure 1. The principle of CEST MRI detection of anticancer drugs, such as gemcitabine.
Exchangeable protons on the drug molecules can transfer RF saturation to the protons of surrounding water (top row), resulting in a decrease in MRI signal. Continuously applying RF pulses leads to the saturation of more water protons, generating a detectable MRI contrast called Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST) contrast (bottom row).