Fig 1. Characterization of QKI-expressing cells in the adult retina (P28).
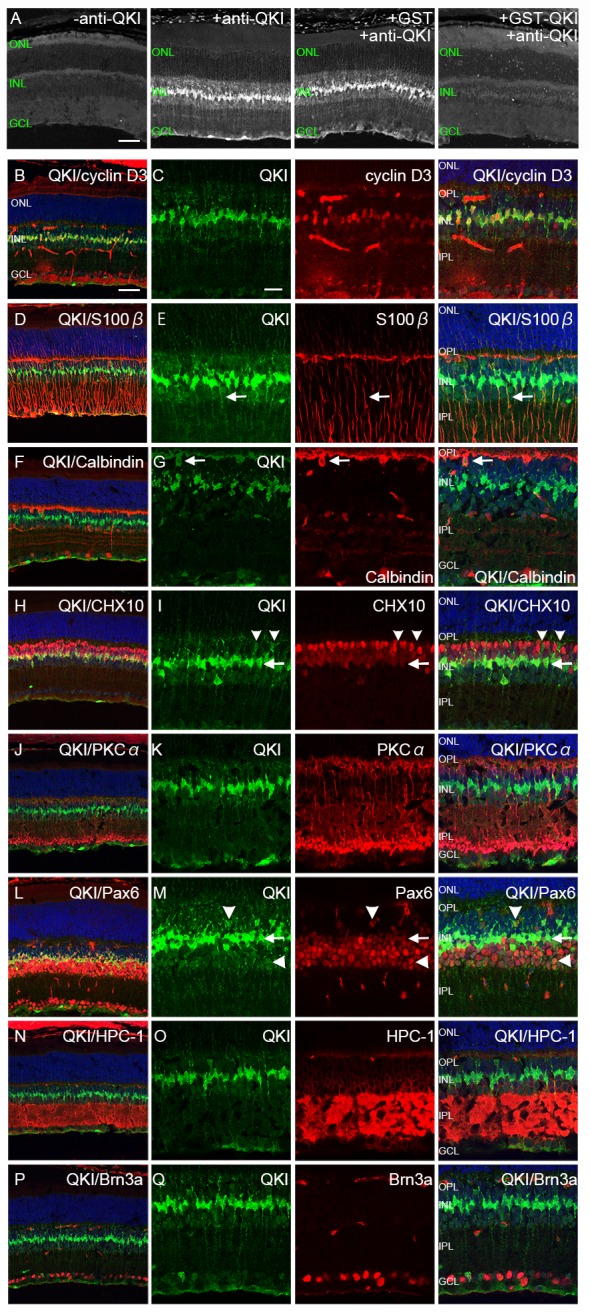
(A) Immunodepletion assay for QKI. Far left is the control without primary antibody. Immunostaining with anti-QKI antibody showed strong signals (middle left). Use of the anti-QKI antibody immunodepleted with GST–QKI (far right) resulted in significantly decreased signals, whereas the anti-QKI antibody incubated with GST showed strong signals by immunostaining (middle right). (B-Q) Retinal sections at P28 were double stained with anti-QKI antibody (green) and retinal markers (red). Nuclei were counterstained with TO-PRO-3 (blue). (B, C) QKI is expressed in the nucleus of Müller glial cells (cyclin D3). (D, E) QKI is expressed in the perinuclear soma of Müller glial cells (S-100ß, [arrows]). (F, G) Weak signals of QKI are expressed in horizontal cells in the INL (calbindin D28k, [arrows]). (H, I) Weak signals of QKI in the INL do not merge with strong Chx10 signals (arrowheads), whereas strong QKI signals merge with weak Chx10 signals (arrows). (J, K) QKI is not localized in the peripheral soma of ON bipolar cells (PKCalpha). (L, M) QKI signals co-localize with weak signals of Pax6 in the center of the INL (arrows), and weak signals of QKI in the inner and outer part of INL co-localize with Pax6 signals (arrowheads). (N, O) Weak signals of QKI in the inner layer of INL are surrounded by those of HPC-1, indicating peripheral soma of amacrine cells. (P, Q) QKI is not co-localized with ganglion cells (Brn3a). ONL, outer nuclear layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; GCL, ganglion cell layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer. Scale bars are 50μm for A, B, D, F, H, J, L, N, and P and 20μm for C, E, G, I, K, M, O, and Q.
