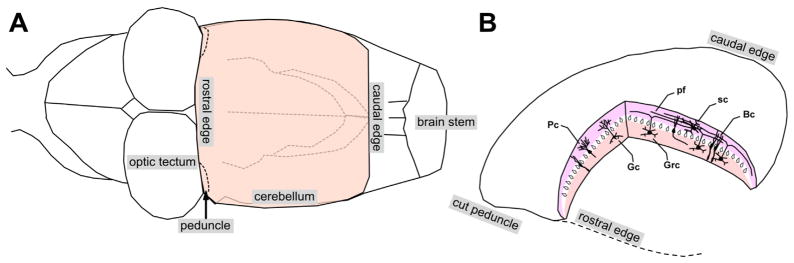
Fig. 1.
Turtle cerebellum. (A) Schematic illustration of the caudal portion of a turtle brain with an intact cerebellum. (B) Cerebellum detached from the rest of the brain at the level of the cerebellar peduncles. Climbing fibers in the peduncle project to the Purkinje cells (Pc). Mossy fibers in the peduncle project to the granule cells (Grc). Grc axons ascend dorsally and bifurcate to form parallel fibers (pf), which make synaptic contacts with the Pc. Bergman cells (BC), stellate cells (sc), Golgi cells (Gc). Dorsal side up.