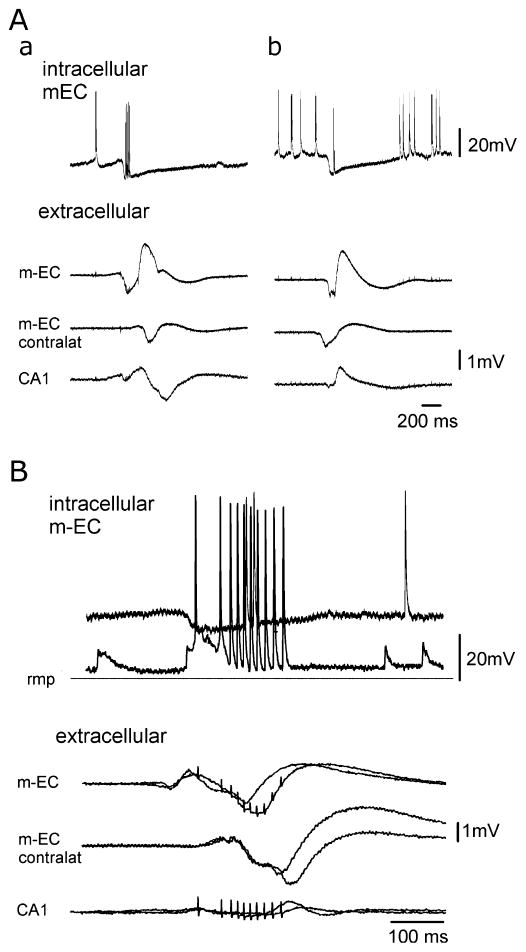
Fig. 8.
Intracellular recordings performed in the m-EC during GABAA-receptor-mediated spontaneous interictal potentials obtained with the simultaneous perfusion of DNQX, AP5 and 4AP. (A) Intracellular (upper traces) and extracellular activities recorded in the m-EC ipsilateral and contralateral to the intracellular recording site and in ipsilateral CA1 during a type 2 potential that initiated in the m-EC (a) and during a GABAergic event that is propagated from the m-EC contralateral to the intracellular recording site (b). The two events were recorded from the same m-EC neuron located in layers II–III. The cell was depolarized to highlight the IPSP that correlates to the GABAergic potential. (B) Superimposed intracellular and extracellular activities recorded in the m-EC ipsilateral and contralateral to the intracellular recording side and in the ipsilateral CA1 during a type 2 GABAergic potential that initiates in the m-EC. The intracellular correlates of two identical GABAergic potentials were recorded at different membrane polarizations during the injection of steady intracellular currents (resting membrane potential, −69 mV) to illustrate the IPSP reversal. Note that action potential firing interrupted the IPSP.