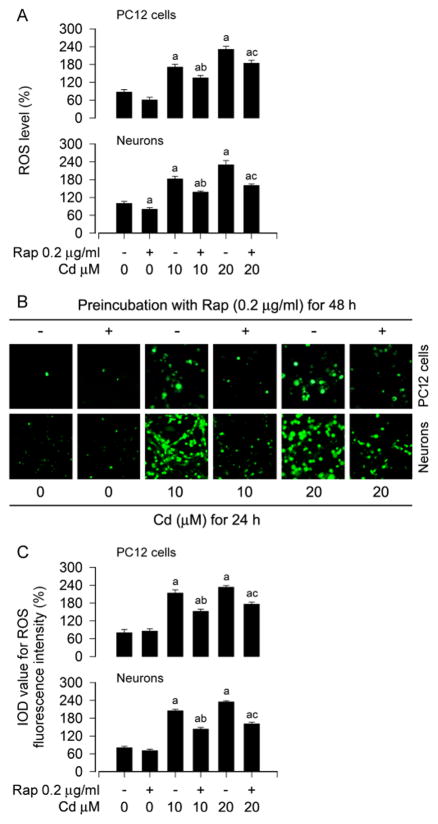
Fig. 1.
Rapamycin attenuates Cd-induced ROS in neuronal cells. PC12 cells and primary neurons were pretreated with rapamycin (Rap, 0.2 μg/ml) for 48 h, and then exposed to Cd (10 and 20 μM) for 24 h, followed by ROS assay and ROS imaging using an oxidant-sensitive probe CM-H2DCFDA. A) Rapamycin attenuated the intracellular ROS production in the cells in response to Cd. B and C) Cd-evoked strong ROS fluorescence (in green) was potently suppressed by rapamycin in the cells. Scale bar: 20 μm. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5). a p < 0.05, difference with control group; b p < 0.05, difference with 10 μM Cd group; c p < 0.05, difference with 20 μM Cd group.