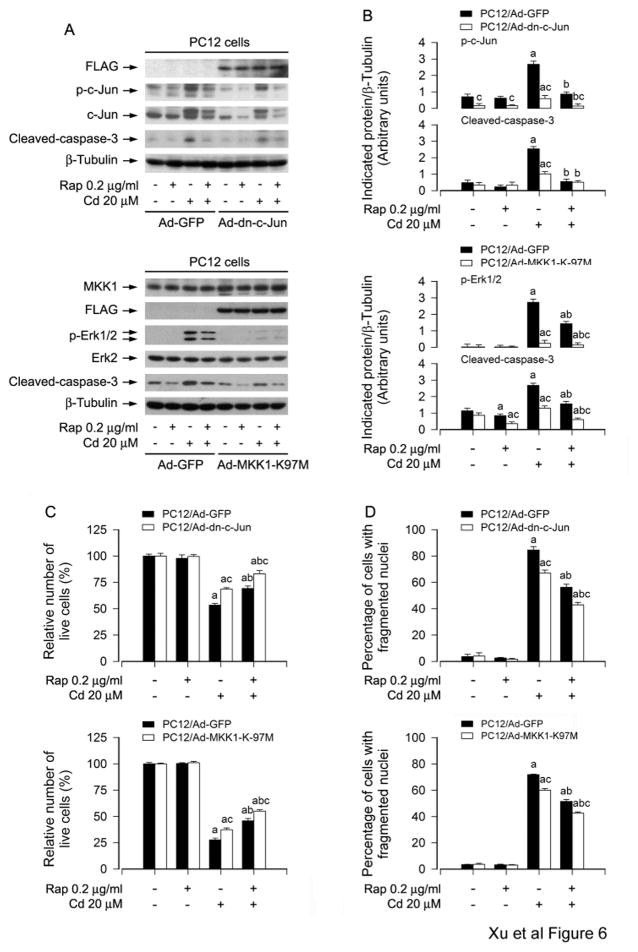
Fig. 6.
Expression of dominant negative c-Jun or dominant negative MKK1 reinforces rapamycin inhibition of Cd-induced neuronal apoptosis. PC12 cells, infected with Ad-dn-c-Jun, Ad-MKK1-K97M and Ad-GFP (as control), respectively, were pretreated with/without rapamycin (0.2 μg/ml) for 48 h, and then exposed to Cd (20 μM) for 4 h (for Western blotting) or 24 h (for live cell analysis, DAPI staining). A) Cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. The blots were probed for β-tubulin as a loading control. B) Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments, and blots for p-c-Jun, p-Erk1/2, and cleaved-caspase-3 were semi-quantified. C) Live cells were detected by counting viable cells using trypan blue exclusion. D) The percentages of apoptotic cells with fragmented nuclei were quantified by DAPI staining. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 3–5). a p < 0.05, difference with control group; b p < 0.05, difference with 20 μM Cd group; c p < 0.05, Ad-dn-c-Jun group or Ad-MKK1-K97M group versus Ad-GFP group.