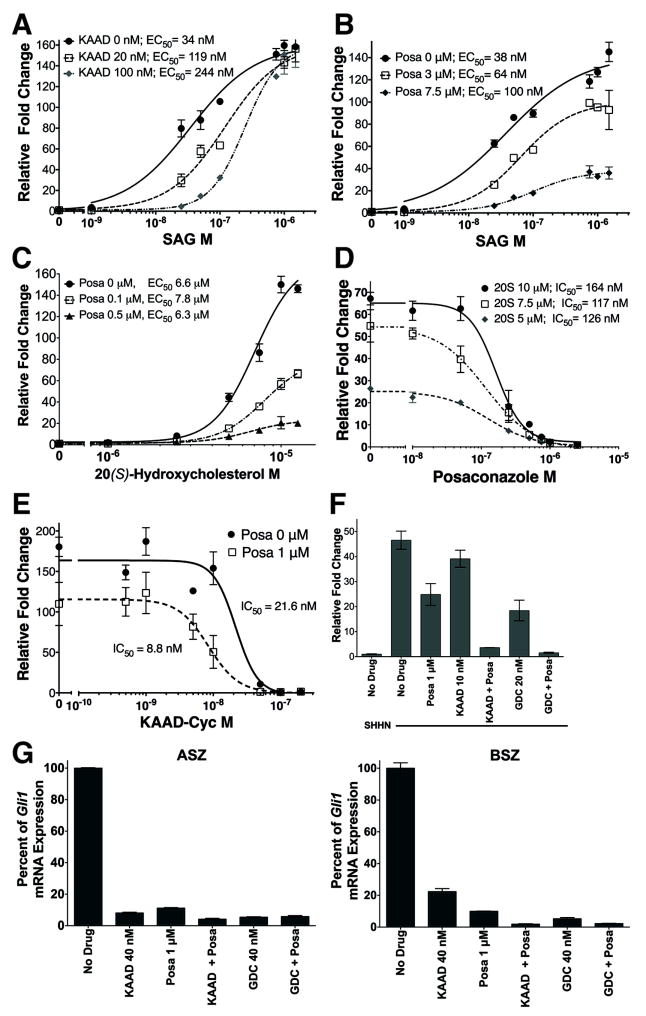
Figure 3. Posaconazole Inhibits The Hh Pathway At Distinct Sites From Other SMO Modulators.
Panels A-F represent signaling assays using SHH-Light2 cells stimulated with SAG, a small molecule SMO agonist, or SHHN CM. (A) Addition of KAAD-cyclopamine 20 nM (1x IC50) and 100 nM (5x IC50) increased the EC50 of SAG ~3.5- and ~7-fold, respectively, while maintaining maximal pathway activation. (B) Treatment with posaconazole 1 μM (~1.1 × IC50) and 7.5 μM (~5.5x IC50) decreased the maximal activity of SAG but did not significantly affect its EC50. (C) Increasing concentrations of posaconazole while titrating 20(S)-hydroxycholesterol, an agonist that binds SMO at a distinct site from SAG, decreased maximal pathway activation of 20(S)-hydroxycholesterol but did not alter its EC50. (D) Increasing concentrations of 20S-hydroxycholesterol, up to 10 μM, did not significantly alter the IC50 of posaconazole. (E) The addition of posaconazole caused a reduction in the IC50 of KAAD-cyclopamine. (F) Treatment with posaconazole 1 μM (~1.1 × IC50), KAAD-cyclopamine 10 nM (~0.5 × IC50) and GDC-0449 20 nM (~1.5 × IC50) partially inhibited Hh pathway activation by SHHN CM. Combination of either KAAD-cyclopamine or GDC-0449 with posaconazole at the same doses further suppressed pathway activation. (G) Treatment of ASZ and BSZ, constitutively active murine BCC cells, with posaconazole 1 μM (~1.1 × IC50), KAAD-cyclopamine 40 nM (~2.0 × IC50) and GDC-0449 40 nM (~3.1 × IC50) significantly inhibited the pathway as measured by Gli1 mRNA. Combination of posaconazole with either KAAD-cyclopamine or GDC-0449 completely inhibited pathway activity. For panels A-E, respective IC50 or EC50 of the titrated compound under varying conditions are listed in the figure. All data represents mean of triplicates +/- S.D.