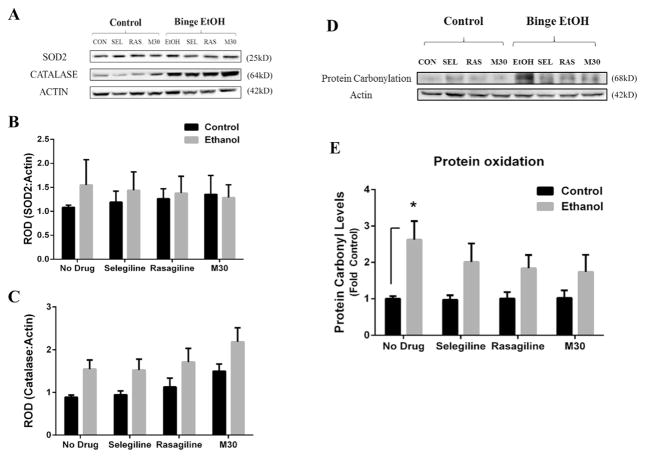
Fig. 4. The effect of binge ethanol and acute MAOI treatment on the expression of oxidative stress enzymes and protein oxidation.
The frontal cortex of rats from all groups were examined for changes in oxidative stress enzymes and protein oxidation levels. Oxidative enzymes were examined by western blot analysis (A). The protein expression levels of SOD2 (B) and catalase (C) were examined in the frontal cortex of control and binge ethanol rats given no drug or a MAOI. Neither binge ethanol nor acute MAOI exposure had any significant effect on the expression of oxidative stress enzymes within individual groups. However, there was a significant group effect for increased catalase expression between control rats vs binge ethanol-exposed rats (p < .0002) and MAOI drug-treated rats vs rats given no drug (p = .026). Oxidized protein was determined by protein carbonylation status of albumin, as represented in (D). Binge ethanol rats displayed a significantly greater degree of protein oxidation compared to control rats (E), but none of the MAOIs examined had any significant effect on reducing protein oxidation levels in either control or ethanol groups. Data presented as mean ± SEM, *p < .05.