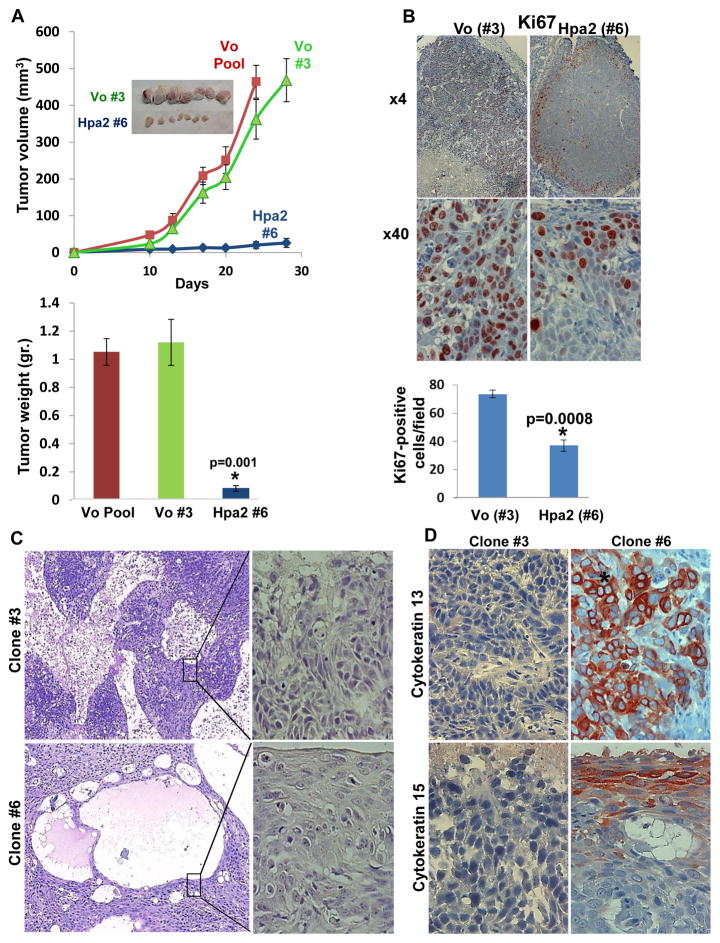
Figure 2.
Marked inhibition of tumor growth by Hpa2 over-expressing cell clones. Cell clones were isolated by limited dilution and clones that showed Hpa2 expression significantly higher than the cell pool were selected for subsequent experiments (#6, #60, #64). Three clones from control (Vo) cells were selected randomly (#3, #5, #8). A. Tumor growth. The indicated clone or pool cells were implanted subcutaneously in SCID mice and tumor growth was inspected over time (A, upper panel). At termination, tumors were collected, photographed (insets), weighed (A, lower panel) and fixed in formalin for histological evaluation. B. Cell proliferation. Five micron sections of control (Vo #3) and Hpa2 over expressing (#6) cell clones were subjected to immunostaining applying anti-Ki67 antibody. Shown are representative photomicrographs at low (×4; upper panels) and high (×40; lower panels) magnifications. Quantification of Ki67-positive cell is shown in the lower panel. C–D. Cell differentiation. Five micron sections of tumor xenografts produced by control (#3) and Hpa2 over expressing (#6) cell clones were subjected to histological evaluation. Shown are representative photomicrographs of H&E staining at low (×4; C, left panels) and high (×40; C, right panels) magnifications. Sections were subjected to immunostaining applying anti-cytokeratin 13 (D, upper panels) and cytokeratin 15 (D, lower panels) antibodies. Note, increased differentiation of tumor cells over expressing Hpa2. Original magnifications: ×40.