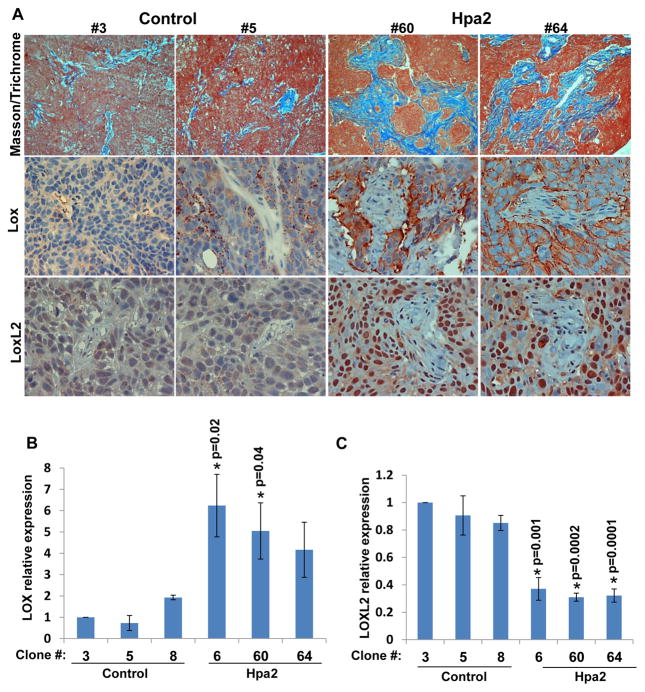
Figure 4.
Hpa2 induces LOX expression and LOXL2 nuclear localization. A. Masson’s/Trichrome and immunostaining. Five micron sections from tumor xenografts produced by the indicated control (#3, #5) and Hpa2 over expressing (#60, #64) cell clones were stained with Masson’s/Trichrome reagents (upper panels). Blue staining denotes collagen type I deposition. Corresponding tumor sections were subjected to immunostaining applying anti-LOX (second panels) and anti-LOXL2 (third panels) antibodies. Note increased collagen deposition by cells over expressing Hpa2, associating with increased LOX levels and nuclear localization of LOXL2. Original magnification: ×40. B–C. Real-time PCR. Total RNA was extracted from the indicated cell clones and corresponding cDNAs were subjected to quantitative real-time PCR analyses. Expression levels of LOX (B) and LOXL2 (C) are shown graphically in relation to the levels in control clone #3 set arbitrarily to a value of 1.