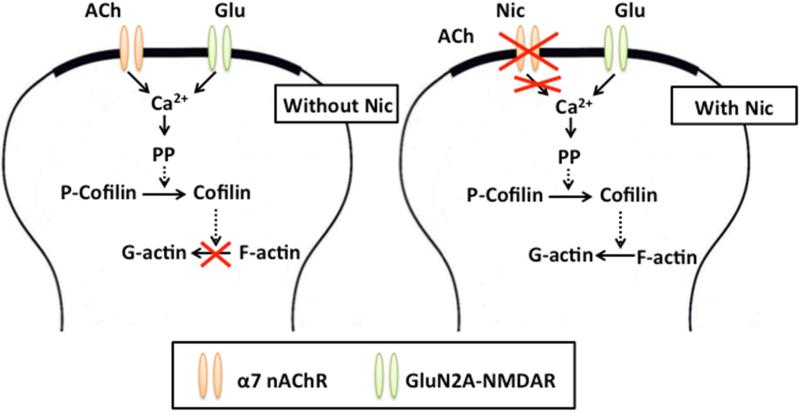
Fig. 7. Possible pathways involved in nicotine-induced depotentiation of consolidated LTP.
GluN2A-NMDARs are activated by glutamate (Glu) released during LFS. (Left) Activation of α7 nAChRs by ACh released during LFS blocks GluN2A-NMDAR-mediated destabilization of F-actin, preventing depotentiation of consolidated LTP. (Right) Nicotine (Nic) desensitizes α7 nAChRs, preventing ACh-induced receptor activation during LFS. In the absence of α7 nAChR-mediated signaling, GluN2A-NMDAR activation destabilizes F-actin, inducing depotentiation of consolidated LTP. The broken arrows indicate that several steps are involved in the signaling process. PP, protein phosphatases; P-Cofilin, phosphorylated cofilin