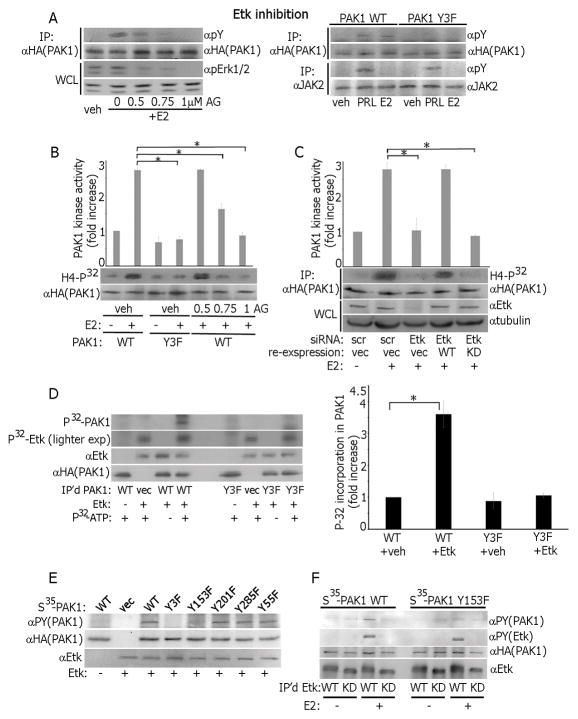
Figure 2.
Etk directly phosphorylates and activates PAK1 in response to estrogen. (A) PAK1 WT cells were treated with Etk inhibitor AG879 before E2 treatment and IP’d PAK1 or whole cell lysate (WCL) were probed with Abs (left panel). PAK1 or JAK2 were IP’d from PAK1 WT and Y3F clones treated with E2 or PRL and immunoblotted (right panel). (B) Cells were treated with AG879. PAK1 was IP’d and subjected to an in vitro kinase assay as in Fig. 1. (C) Cells were transfected with control (scr) or Etk siRNA. In siRNA rescue experiments, 24h after Etk siRNA transfection, cells were transfected with either Etk WT or Etk kinase-dead mutant (KD). PAK1 was IP’d and subjected to in vitro kinase assay as in Fig. 1. (D) PAK1 WT and Y3F were IP’d and assessed in the in vitro kinase assay in the presence of recombinant active Etk. The levels of P32 incorporation in PAK1 were plotted. (E) PAK1 WT and indicated tyrosine-deficient PAK1 mutants were translated in vitro and subjected to the in vitro kinase assay in the presence of recombinant Etk and non-radioactive ATP. (F) WT or kinase-dead (KD) Etk were IP‘d from the cells treated with/without E2 and assessed in the in vitro kinase assay in the presence of either PAK1 WT or Y153F as in E. Each figure represents the same blot reblotted with the indicated antibodies. All blots are representative of at least 3 experiments.*, p<0.05, n=3.