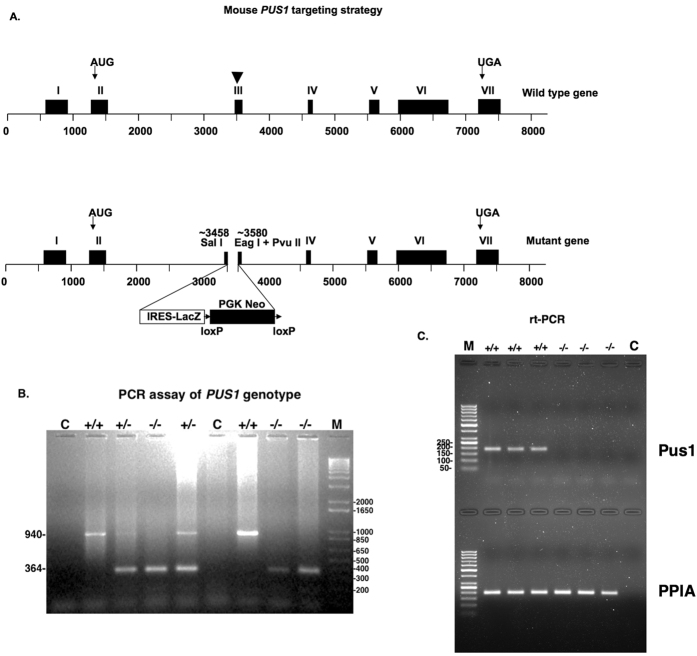
Figure 1. Mouse Pus1 gene targeting strategy and assay of genotype.
In panel (A) the targeting strategy is presented with a diagram of the wild-type gene on the top, indicating the positions of the initiator codon in exon II and the stop codon in exon VII with arrows. Exon III is indicated with an arrowhead because this exon contains the codon for the Asp that is essential for activity (see Results). This exon was targeted for disruption and the resulting mutant gene is shown in the lower diagram. In panel (B) an example of an ethidium bromide-stained gel employed to determine the genotypes of the mice is shown. The lane labeled C denotes a control where no DNA was added to the PCR reaction, +/+ is the result when DNA from wild-type mice is used, +/− is the result when DNA from heterozygous mice is used, and −/− is the result when DNA from homozygous mutant mice is used. M denotes the 1Kb+ marker (Promega, Madison, Wisconsin) with sizes in bp on the right. The sizes the bands resulting from the wild-type (940 bp) and mutant (364 bp) genes are indicated on the left of the panel. In panel (C) a 1.5% agarose gel stained with ethidium bromide showing the results of real time-PCR reactions of mRNA from three Pus1+/+ and three Pus1−/− mice with primers specific for Pus1p mRNA in the top portion of the gel and primers specific for PPIA in the bottom portion. The marker in the far-left lanes is the GeneRuler 50 bp DNA ladder (Life Technologies) with sizes represented on the left in the top portion. The far right lanes in both portions of the gel are the results of using no cDNA in the PCR reaction.