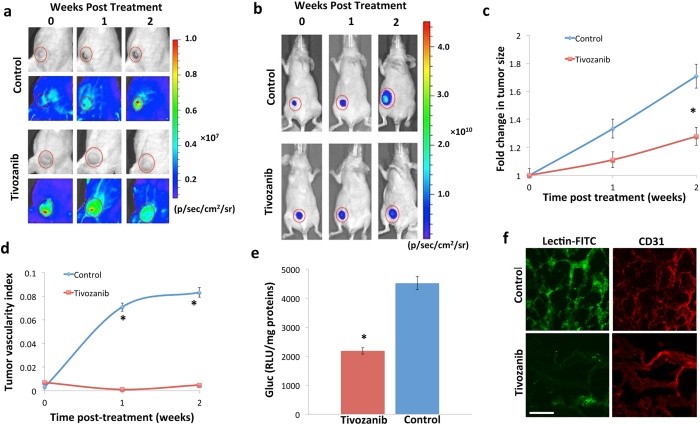
Figure 2. Bioluminescence imaging of tumor vascularity and response to anti-angiogenic therapy.
Mice were subcutaneously implanted with 106 U87-Fluc cells and one week later, randomized and treated with either vehicle (control) or tivozanib daily for 2 weeks (n = 6/group). (a) Mice were imaged for tumor vascularity after injection of rGluc followed by coelenterazine. (b) Tumor volume was monitored after injection of D-luciferin, the Fluc substrate. A representative mouse from each group is shown. (c) Tumor size was measured weekly using a manual caliper and average fold changes in tumor size was calculated. (d) Tumor vascularity index (ratio of tumor rGluc signal to Fluc signal) was calculated at different time points. Results are represented as mean ± SD (*P < 0.05). (e) Ex vivo rGluc activity was analyzed in tumor homogenates using a luminometer after addition of coelenterazine. Results are represented as mean of rGluc activity in relative luminescence units (RLU) in tumor homogenates (normalized to total protein) ± S.D (*P = 0.03). (f) Mice from both groups were injected with Fluorescein-lectin and tumors were excised, sectioned and evaluated for Fluorescein (vascular endothelium) or immunostained with anti-CD31 antibody and analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar, 50 μm.