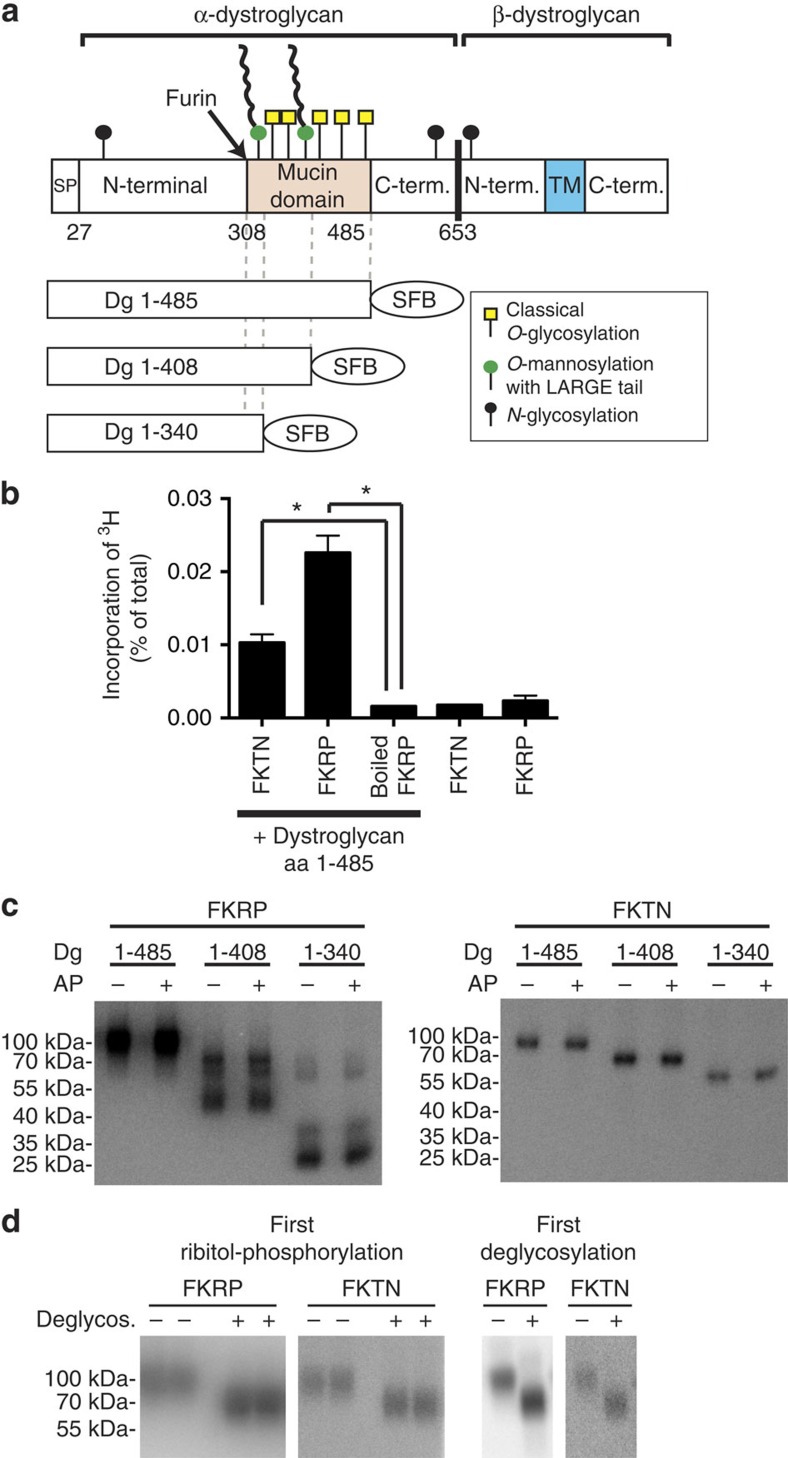
Figure 5. FKTN and FKRP can transfer ribitol phosphate to recombinant α-dystroglycan.
(a) Schematic representation of α-dystroglycan fragments used in this study. (b) Transfer of [3H]-ribitol from CDP-[1-3H]-ribitol to α-dystroglycan (∼1 μg) by recombinant FKTN and FKRP (∼0.1 and ∼0.4 μg, respectively). After incubation for 16 h at 30 °C, proteins were recovered using streptavidin beads and incorporated radioactivity was determined with a scintillation counter. Values are means±s.d. of three biological replicates from one representative experiments out of three. Asterisks indicate P<0.05 in Student's t-test. (c) Incorporation of [32P] from [32P]-CDP-ribitol to different fragments of α-dystroglycan by FKTN and FKRP. After 16 h of incubation at 30 °C, proteins were incubated with (+) or without (−) alkaline phosphatase (AP) and resolved by SDS–PAGE. 32P was detected with a storage phosphorimager. (d) Effect of deglycosylation of α-dystroglycan (aa 1–485) with a ‘deglycosylation mix' on the incorporation of radioactivity from [32P]-CDP-ribitol catalysed by FKRP or FKTN. The deglycosylation treatment of α-dystroglycan performed either before (two left panels) or after (two right panels) ribitol-phosphorylation decreased the apparent molecular weight of α-dystroglycan, but did not reduce the incorporated radioactivity.