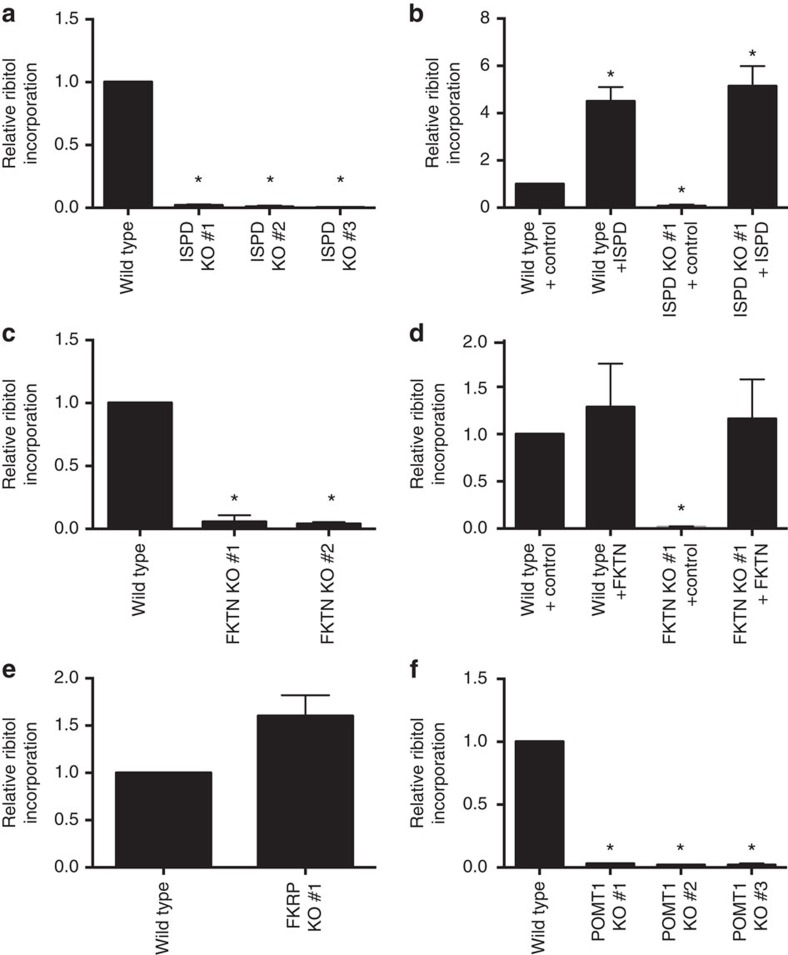
Figure 6. Incorporation of ribitol in α-dystroglycan in cells depends on ISPD, FKTN and POMT1.
(a–f) An α-dystroglycan fragment (comprising amino acids 1–485 and a C-terminal SFB-tag) was purified by affinity chromatography from cell culture supernatants of HEK293 clones, in which the genes indicated in the figure had been inactivated. N- and O-glycans were released under non-reducing conditions, hydrolysed and derivatized with TMS before analysis by GC-MS to assess ribitol incorporation, which was normalized to methyl-glycine concentrations. Means and s.e.m. of 3–6 independent experiments are shown, and values were normalized within each experiment to levels in wild-type (control) cells. Asterisks indicate P<0.05 obtained from Dunnett's multiple comparisons test, compared with wild type or wild-type control cells. ISPD or FKTN knockout clones (a,c), as well as one ISPD (b) and one FKTN (d) knockout clone complemented or not with mouse Ispd (b) or Fktn (d) cDNA were analyzed. One FKRP clone (e) and three different POMT1 knockout clones (f) were analysed.