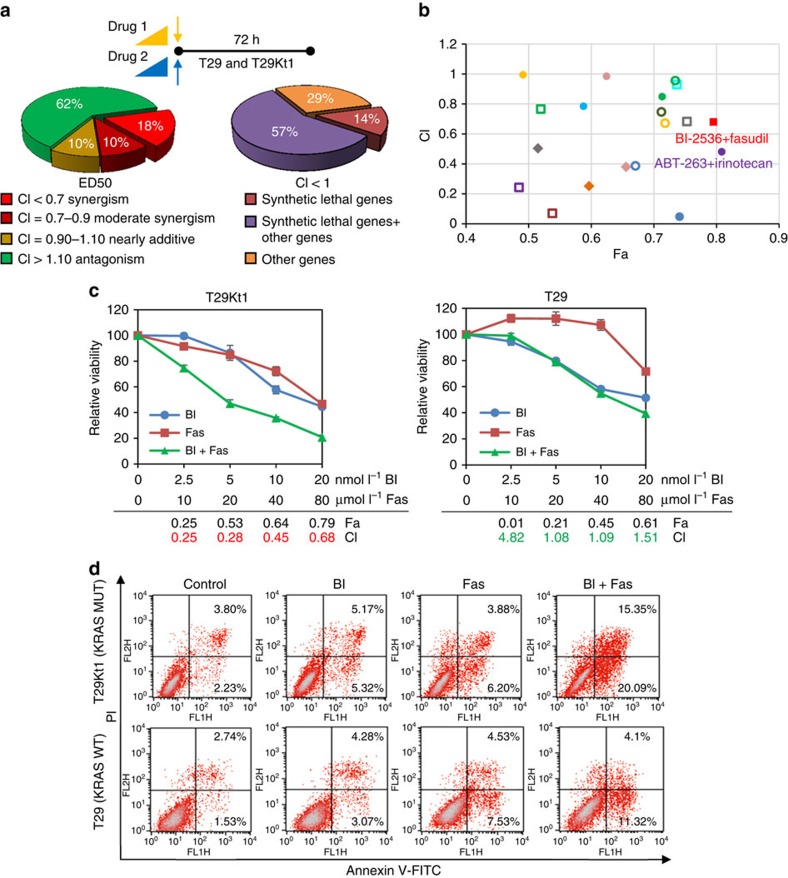
Figure 1. A synthetic lethal chemical screen reveals that KRAS-mutant cells are selectively sensitive to the combined inhibition of PLK1 and ROCK.
(a) Schematic of the combinations tested and the drug interaction signatures. Twenty clinical drugs were tested in pairwise combinations (a total of 190 pairs) in T29Kt1 cells harbouring a KRAS mutation. Drugs were added at a relevant fixed ratios (IC50 ratios, see also Supplementary Table 1) at four concentration combinations in each representative drug pair. The cell viability was determined. Left: compilation of the total number of drug pair synergies, moderate synergies, nearly additive interactions and antagonistic interactions. The combination index (CI) was calculated using CalcuSyn software (Version 2; Biosoft) as described in the Methods section. Right: the frequencies at which the drug target gene types appear in the synergy cluster (CI<1). The oncogenic KRAS synthetic lethal genes accounted for the largest proportion of synergies specific to KRAS-mutant cells. (b) The Fa–CI plot. The Fa (fraction affected by the dose) and CI value of two drugs at their combination of IC50's were listed in X and Y axes and synergistic pairs with CI<1 were shown. The combination of BI-2536 and fasudil exhibited leading therapeutic efficacy and applicable potential. (c) The cytotoxicity of BI-2536 and fasudil. T29Kt1 and T29 cells were incubated with increasing concentrations of BI-2536 (BI) and fasudil (Fas) alone or in combination for 72 h, and the cell viability was determined. The CI and Fa values for the combination of BI-2536 and fasudil were calculated. The averages and error bars represent the mean±s.d. from three independent experiments. (d) Percentage of apoptotic cells was determined by Annexin-V and propidium iodide staining after BI-2536 (10 nmol l−1) and fasudil (40 μmol l−1) treatment alone or in combination for 72 h in T29Kt1 and T29 cells.