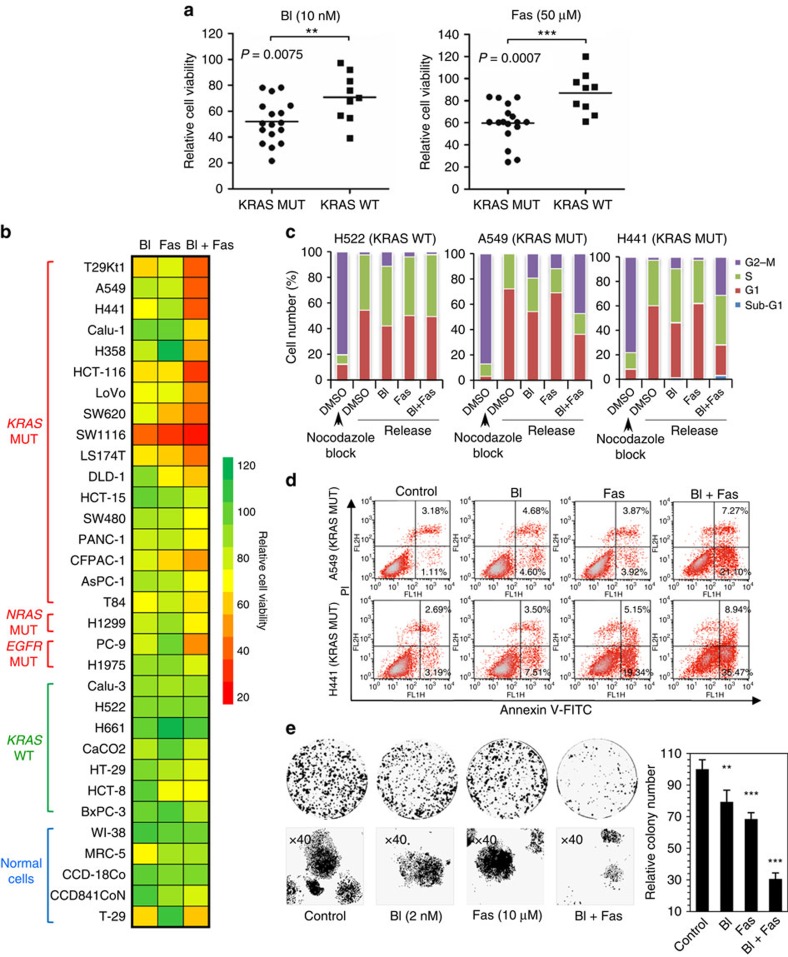
Figure 2. KRAS-mutant cancer cells are significantly sensitive to the pharmacologic inhibition of PLK1 and ROCK.
(a) Seventeen KRAS-mutant (KRAS MUT) and nine wild-type (KRAS WT) cancer cell lines were treated with the indicated concentrations of BI-2536 or fasudil for 72 h; the dots represent the cell viability normalized to no drug treatment. The bars indicate the means. Student's t-tests were performed between the MUT and WT groups; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (b) Thirty-two cell lines carrying different KRAS genotypes were treated with BI, Fas or the combination of BI and Fas for 72 h. The percentage of viable cells was colour coded in a heatmap. (c) H522 (KRAS WT), A549 (KRAS MUT) and H441 (KRAS MUT) cells were treated with BI-2536 (2 nmol l−1), fasudil (10 μmol l−1) or the combination (BI-2536+fasudil) for 48 h after synchronization and release. The cell cycle distribution was analysed by flow cytometry using propidium iodide staining. (d) A549 and H441 (KRAS MUT) cells were treated with BI-2536 (2 nmol l−1), fasudil (10 μmol l−1) or a combination of BI and Fas for 72 h, and the percentage of apoptotic cells (Annexin positive) was determined by Annexin-V and propidium iodide staining. (e) A549 cells (1,000) were plated in 60-mm dishes and treated with dimethylsulphoxide, BI-2536 (2 nmol l−1), fasudil (10 μmol l−1) or a combination of BI and Fas for 7 days. The cell colonies were stained with crystal violet and counted. The relative number of colonies was calculated by normalization to control as 100%. The values represent the mean±s.d. of three independent assays; Student's t-tests were performed; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. MUT, mutant; WT, wild type.