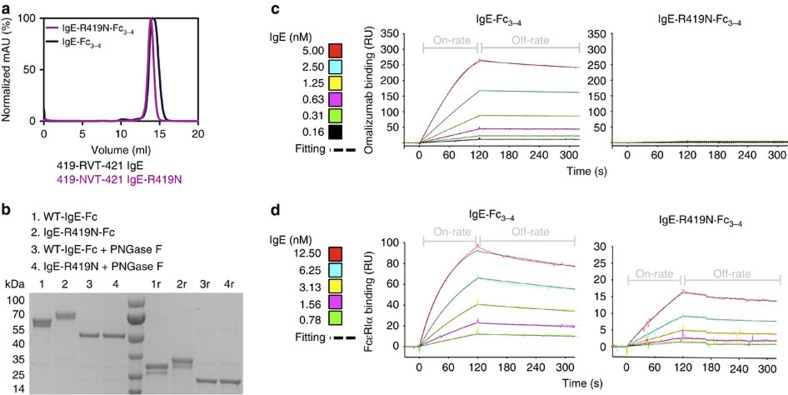
Figure 5. A single IgE mutation prevents omalizumab binding.
(a) The IgE-Fc3–4 point mutant, R419N, contains a novel glycosylation consensus sequence and is expressed as a soluble monomer as assessed by gel filtration chromatography of IgE-R419N-Fc3–4 and IgE-Fc3–4 species. (b) SDS–PAGE analysis of non-reduced and reduced (‘r') IgE-R419N-Fc3–4, and IgE-Fc3–4, demonstrates that the R419N mutation induces an additional glycosylation event and a mass shift of ∼2 kDa per IgE chain. PNGaseF treatment removes all N-linked glycans, and demonstrates that the mass shift in the IgE-R419N-Fc3–4 protein arises from N-linked glycosylation. (c,d) SPR-binding assays with immobilized omalizumab (c) or FcɛRIα (d) show that IgE-R419N-Fc3–4 is unable to bind omalizumab, but exhibits binding to FcɛRIα at nM concentrations.