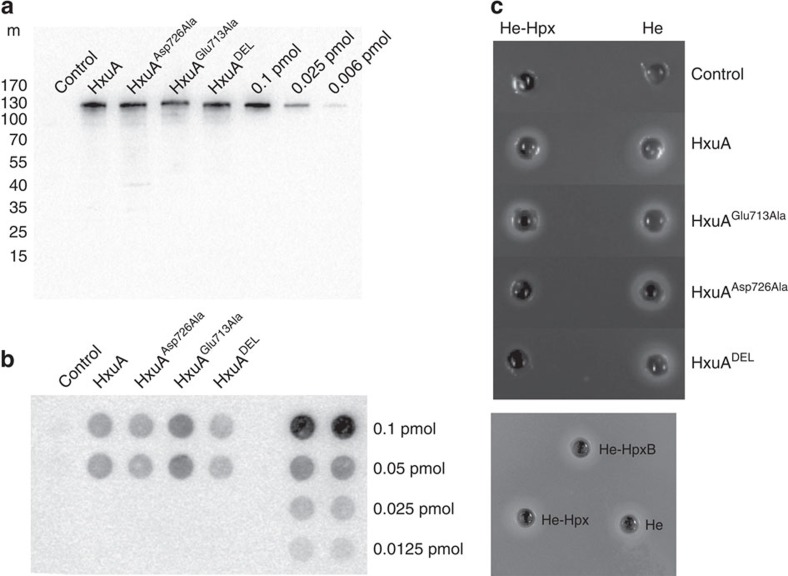
Figure 5. Phenotypes of HxuA mutants.
(a) Amount of HxuA in the various strains, as detected by immunoblotting with anti-HxuA antibodies on whole-cell contents analysed by SDS-PAGE (control, WTHxuA, HxuAAsp726Ala, HxuAGlu713Ala and HxuADEL). The equivalent of 0.05 OD600nm (107 cells) was deposited in each lane. Known amounts of purified HxuA were run alongside. The scale on the left (m) represents molecular weight in kDa. (b) Detection of interaction of biotinylated haemopexin with HxuA and its mutants in whole cells by dot-blot analysis in vivo (control, wild-type, HxuAAsp726Ala, HxuAGlu713Ala, HxuADEL). Samples were spotted in duplicate. The equivalent of 0.05 OD600nm (107 cells) was deposited in each spot, in duplicate. Known amounts of purified biotinylated haemopexin were run alongside, in duplicate. (c) Analysis of the in vivo activities of HxuA, HxuADEL, HxuAGlu713Ala and HxuAAsp726Ala, in haem acquisition tests from haem and haem-haemopexin. Each well contained 100 μl of either 5 μM haem (He) or 5 μM haem-haemopexin (He-Hpx). The bottom panel shows the same activity test for haem (He), haem-haemopexin (He-Hpx) and the biotinylated haem-haemopexin (He-HpxB) for WT strain.