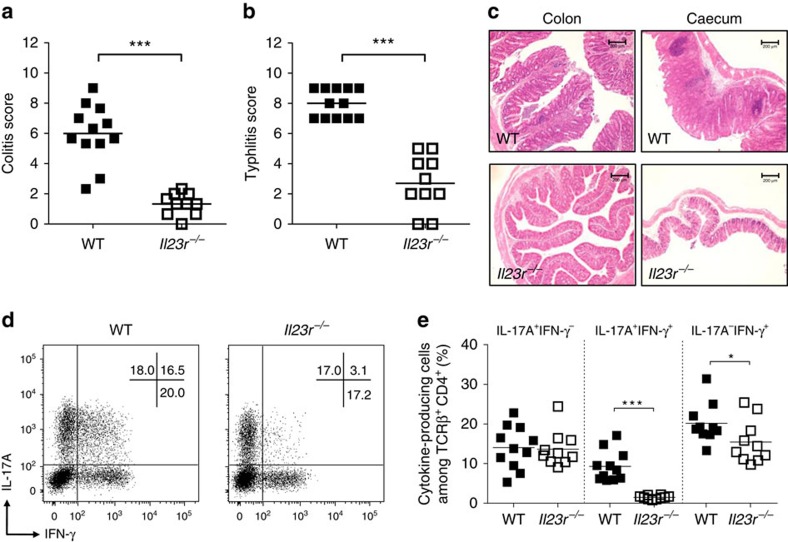
Figure 1. IL-23 signalling is required for bacteria-driven T-cell-dependent colitis and the emergence of IL-17A+IFN-γ+ T cells.
C57BL/6 WT and Il23r−/− mice were infected orally with Hh and received weekly i.p. injections of IL-10R blocking antibody. Mice were killed at 4 weeks post infection and assessed for intestinal inflammation. (a) Colitis scores. (b) Typhlitis sores. (c) Representative photomicrographs of colon and caecum (× 10 magnification; scale bars, 200 μM). (d) Representative flow cytometry plots of colonic lamina propria gated on viable CD4+ T cells. (e) Frequencies of IL-17A+ and/or IFN-γ+ CD4+ T cells present in the colon. Data represent pooled results from two independent experiments (n=12 for WT, n=10 for Il23r−/−). Bars are the mean and each symbol represents an individual mouse. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 as calculated by Mann–Whitney U test.