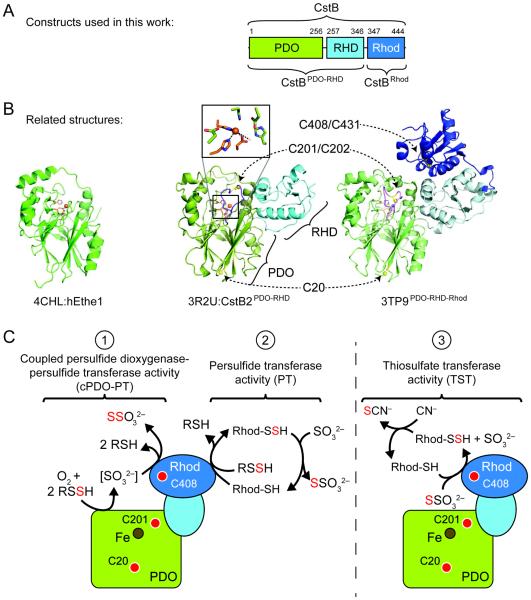
Figure 2.
Structural overview of CstB and related enzymes. (A) Domain organization of S. aureus CstB, with N-terminal persulfide dioxygenase (PDO) domain, middle rhodanese homology domain (RHD), and C-terminal rhodanese domain (Rhod). (B) Structures of CstB homologs previously published or from structural genomics efforts: hETHE1 (PDB 4CHL, left panel), S. aureus COL CstB2PDO-RHD (PDB 3R2U, middle panel), and A. acidocaldarius homolog of unknown function (PDB 3TP9, right panel). PDO domains are shaded green, RHD in light blue, and rhodanese domains in dark blue. Conserved metal-binding side chain ligands are highlighted in orange and conserved cysteines in yellow. The extended loop containing C201 that is not present in hETHE1 is highlighted in purple in the other two structures. (C) Cartoon model of S. aureus CstB highlighting the three catalytic activities documented here: coupled persulfide dioxygenase-persulfide transferase (cPDO-PT) activity, reaction 1; persulfide transferase (PT) activity, reaction 2; rhodanese or thiosulfate transferase (TST) activity, reaction 3. Approximate locations of conserved cysteines and Fe center are indicated by the red and brown circles, respectively. In all panels, the PDO domain is shaded green, RHD light blue, and Rhod domain dark blue.