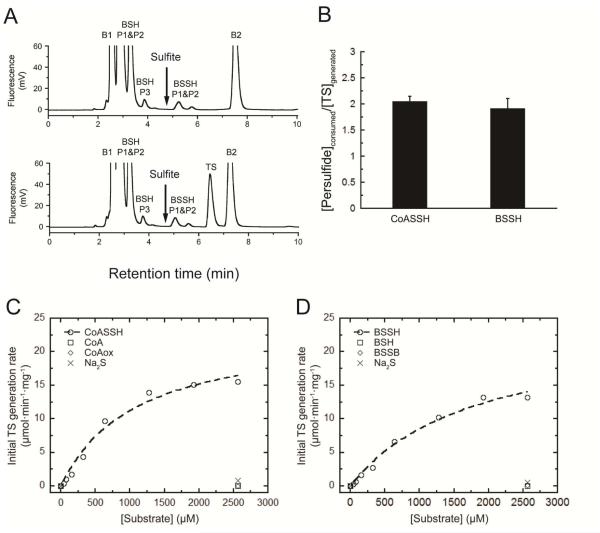
Figure 3.
Coupled persulfide dioxygenase-persulfide transferase (cPDO-PT) activity of CstB with various persulfide substrates. (A) Representative LC-based assays used to measure reactant-product profiles of cPDO-PT activity with BSSH at t=0 min (top trace) and t=2 min (bottom trace) as substrates at 400 nM CstB. The chromatographic position of sulfite is indicated by the arrow.15 Note that B1 and B2 peaks are from labeling buffer; labeled BSH displays as two major peaks (BSH P1&P2) and one minor peak; BSSH is highly unstable in aerobic buffer used here to lyse the cells and thus is underestimated as two small peaks (BSSH P1 & P2). The concentration was alternatively measured using a cold cyanolysis assay.17 (B) Stoichiometry of persulfide substrates consumed (CoASSH and BSSH) versus TS generated for cPDO-PT activity of CstB. The molar ratio of CoASSH consumed to TS generated is ≈1.9 and BSSH consumed to TS generated is ≈2.1 in in multiple experiments carried out at 400 nM CstB. (C) Initial TS generation rates as a function of concentrations of CoASSH (open circles) vs. CoA (open squares), CoAox (open diamonds) and Na2S (crosses). The dashed, continuous line through the open circles is a fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation, with parameters summarized in Table 2. (D) Initial TS generation rates as a function of the concentrations of BSSH (open circles) vs. BSH (open squares), BSSB (open diamonds) and Na2S (crosses). The dashed, continuous line through the open circles is a fit to the Michaelis-Menten equation, with parameters summarized in Table 2.