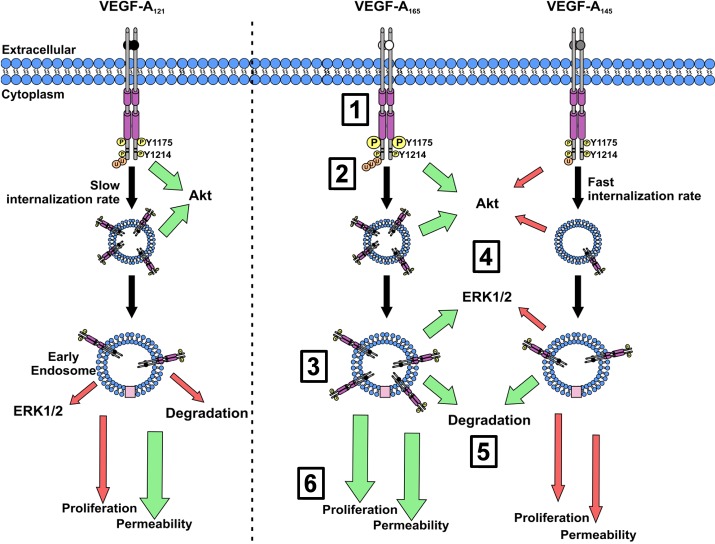
Fig. 6.
Schematic depicting VEGF-A isoform-specific VEGFR2 trafficking and downstream signaling transduction. Upon ligand binding (1) VEGFR2 undergoes dimerization and either differential (Y1175) or comparable (Y1214) trans-autophosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues, depending on the VEGF-A isoform used. (2) This results in distinct levels of receptor ubiquitylation (3) and internalization into EEA1-positive early endosomes. (4) Differential levels of VEGF-A isoform-stimulated VEGFR2 internalization impacts on Akt and ERK1/2 activation in combination with VEGFR2-Y1175 phosphorylation. (5) From early endosomes VEGFR2 is trafficked into late-endosomes where it under goes VEGF-A isoform-specific proteolysis prior to lysosomal degradation. (6) VEGF-A isoform-specific VEGFR2 activation and receptor trafficking, mediates their individual capacities to regulate endothelial cell permeability, proliferation and blood vessel formation. Size and magnitude of arrow denotes magnitude of response; red, reduced; green, increased.