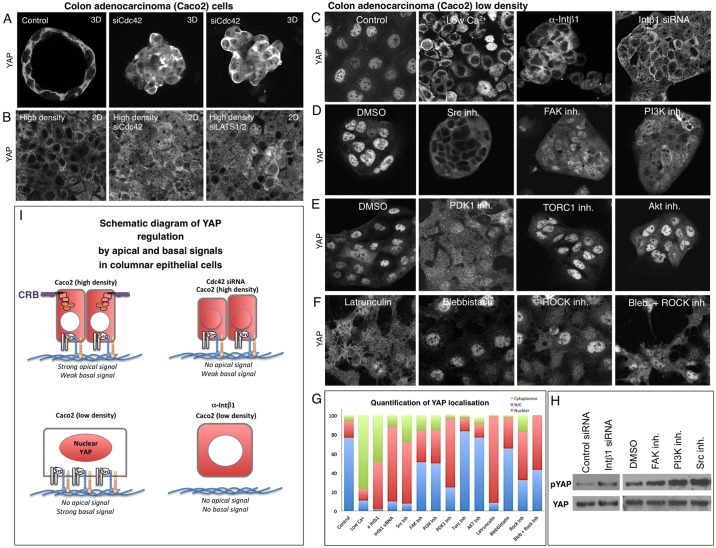
Fig. 7.
Basal integrin-Src signalling promotes YAP nuclear localisation in human Caco2 epithelial cells when apical domain formation is blocked. (A) Caco2 colon adenocarcinoma cells form 3D cysts in cell culture that feature cytoplasmic YAP localisation. Silencing of CDC42 by siRNA knockdown disrupts apical-basal polarity and induces more nuclear YAP localisation. (B) Caco2 colon adenocarcinoma cells form 2D epithelial monolayers at high density. Silencing of CDC42 by siRNA knockdown disrupts apical-basal polarity and induces more nuclear YAP localisation, similar to silencing of LATS1/2. (C) YAP nuclear localisation is very strong when Caco2 cells are plated at low density to prevent apical domain formation. Nuclear localisation is prevented by treatment of Caco2 cells with low-calcium medium, anti-ITGB1 antibodies (PD52) or by ITGB1 siRNA treatment, but not in controls. (D) YAP nuclear localisation is prevented by treatment of Caco2 cells with the Src inhibitor Dasatinib, by the FAK inhibitor PF573228 or by the PI3K inhibitor GDC0941, but not by treatment with DMSO solvent. (E) YAP nuclear localisation is reduced by treatment of Caco2 cells with the PDK1 inhibitor BX795, but not by the AKT inhibitor MK2206, TORC1 inhibitor Everolimus or DMSO solvent. (F) YAP nuclear localisation is reduced by treatment of Caco2 cells with the F-actin destabilising drug Latrunculin, the myosin II inhibitor Blebbistatin or the Rho kinase inhibitor Y27632, or a combination of Blebbistatin and Y27532. (G) Quantification of C-F. (H) Western blotting analysis of p-YAP levels in Caco2 cells treated with control siRNAs or ITGB1 siRNAs, as well as DMSO control, FAK inhibitor, PI3K inhibitor or Src inhibitor. Total YAP levels are shown as a control. (I) Schematic diagram of YAP regulation in Caco2 cells.