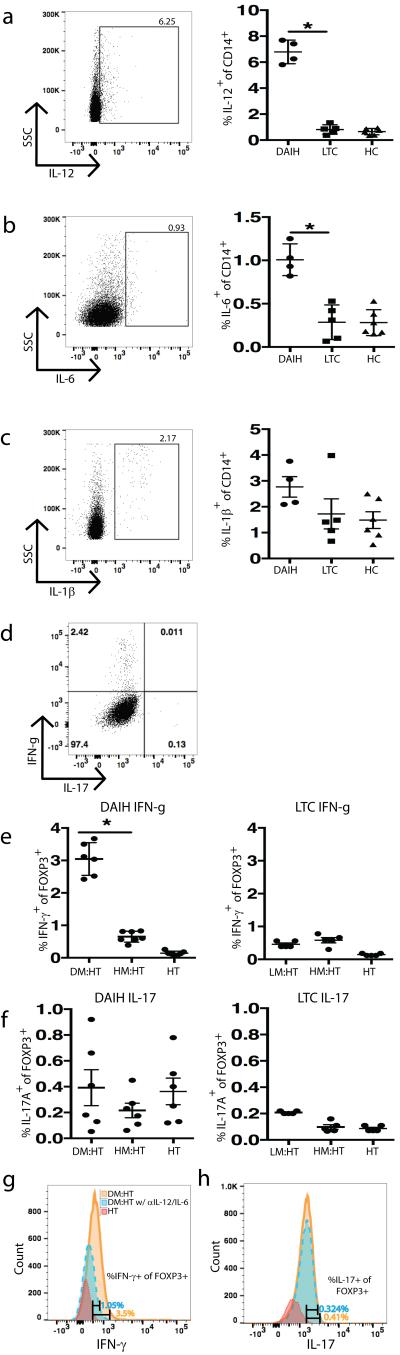
FIGURE 5.
Monocytes from subjects with de novo autoimmune hepatitis secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines inducing TH1 cells. Monocytes from the subjects with de novo autoimmune hepatitis (n=4), liver transplanted subjects without de novo autoimmune hepatitis (n=5) and healthy non-transplanted subjects (n=6) were stimulated with LPS for 24-hours and stained with anti-CD3, anti-CD14, intracellular cytokines IL-12, IL-6 and IL-1β. Cytokine secretion analyzed using flow cytometry.
CD14+ monocytes from healthy non-transplanted subjects (n=6), liver transplanted subjects without de novo autoimmune hepatitis (n=5) and subjects with de novo autoimmune hepatitis (n=6) were co-cultured with sorted Tregs from healthy non-transplanted subjects in the presence of plate bound anti-CD3 for 5-days and IL-17A and IFN-γ secretion from FOXP3+ Tregs was assessed using flow cytometry. CD14+ monocytes from a subject with de novo autoimmune hepatitis were co-cultured with sorted Tregs (CD4+CD25hiCD127−) from a healthy non-transplanted subject in the presence of anti-IL-12, anti-IL-6, and plate bound anti-CD3 for 5-days and IL-17A and IFN-γ secretion from FOXP3+ Tregs was assessed using flow cytometry.
A-C) Increased IL-12 and IL-6 secretion from monocytes of subjects with de novo autoimmune hepatitis (dAIH) (p=0.01 for IL-12 and IL-6). IL-1β secretion not significantly different between the three patient groups.
D) Representative histogram for co-culture of Tregs isolated from healthy non-transplanted subjects (HC) with monocytes from subjects with dAIH.
E-F) monocytes from subjects with dAIH induce IFN-γ (but not IL-17A) secretion from FOXP3+ Tregs of HC (p=0.03), however monocytes from liver transplanted subjects without de novo autoimmune hepatitis (LTC) fail to induce significant amounts of IFN-γ and IL-17A secretion from FOXP3+ Tregs of HC. (DM: dAIH monocytes; HM: HC monocytes; HT: HC Tregs; LM: LTC monocytes)
G-H) monocytes from a subject with de novo autoimmune hepatitis induce IFN-γ (but not IL-17A) production from FOXP3+ Tregs of a healthy control, however in the presence of anti-IL12, this induction of IFN-γ is inhibited. Blockade with anti-IL-6 has no influence on IL-17A production.