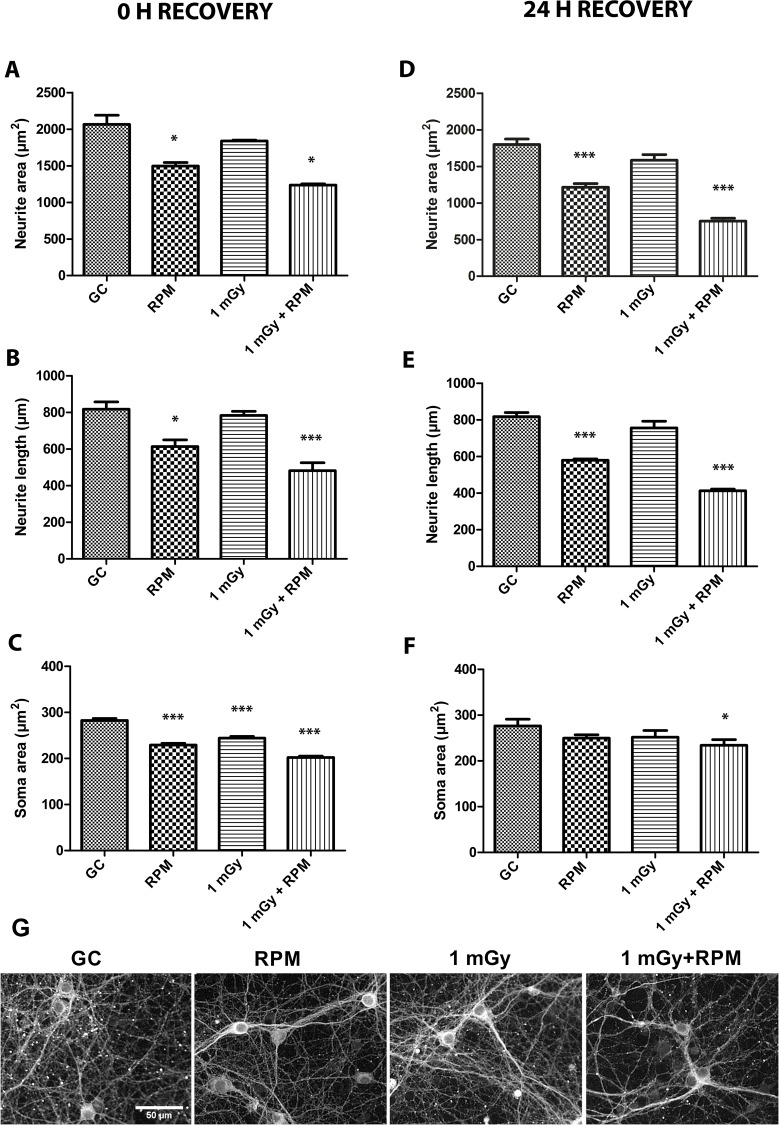
Fig 4. Neuronal morphology is altered after chronic RPM and irradiation exposure, and after ground recovery.
(A, B, C) Morphometric analyses on βIII tubulin stained neurons immediately after 5-day chronic exposure conditions unveiled a significantly decreased neurite area (A) and neurite length (B) after RPM exposure and after combined RPM and radiation exposure. Analysis of the soma area revealed a strong decrease in soma area after all exposure conditions (RPM, irradiation and co-exposure) (C). (D, E, F) Morphometric analyses after a 24 h ground recovery period showed a persistent and similar reduction in neurite area (D) and length (E) after radiation and/or RPM exposure, while the soma area was shown to be mostly recovered to control levels in RPM or radiation exposed neurons after 24 h recovery (F). (G) Fluorescent images of neuronal network cultured exposed to ground conditions (GC), RPM, 1 mGy and 1 mGy combined to RPM. RPM = random positioning machine, GC = ground conditions, Gy = Gray. Values are represented as mean±SEM. N = 3, * p<0.05, *** p<0.001. Asterisks represent differences between RPM/irradiation groups and ground controls (GC).