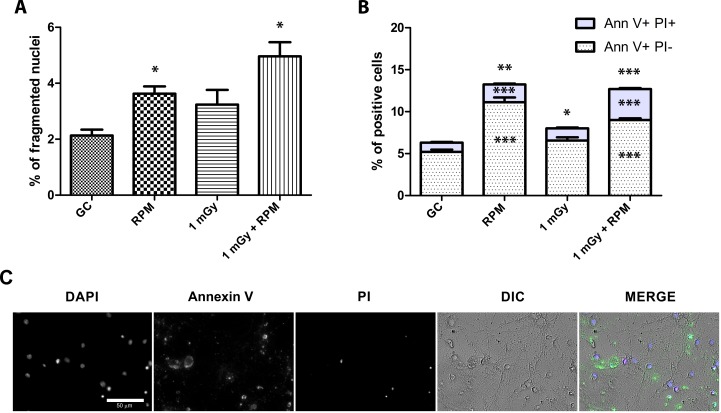
Fig 5. Co-exposure to chronic radiation and RPM results in a synergistically increased percentage of late-apoptotic neurons.
(A) Analysis of the percentage of fragmented nuclei revealed a significant increase in apoptosis after RPM and combined exposure, but not after chronic exposure to radiation alone. (B) An Annexin V/PI apoptosis assay unveiled an increase in the total number of apoptotic cells (AnnV+/PI+ + AnnV+/PI-) in all conditions. However, when separately investigating early and late apoptosis, AnnV+/PI+ and AnnV+/PI- labeled neurons were increased only after RPM and after combined exposure. Finally, only AnnV+/PI+ labeled neurons, representing late apoptotic neurons, were shown to be synergistically increased after combined exposure. (C) Nuclei, Annexin V, propidium iodide (PI), differential interference contrast (DIC) and merge representative images of neuron culture exposed to ionizing radiation and RPM. GC = Ground controls, RPM = random positioning machine, Gy = Gray. Values are represented as mean±SEM. N = 3, * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Asterisks represent differences with non-exposed controls (GC).