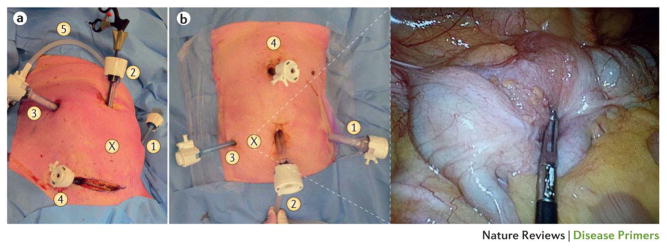
Figure 5. Laparoscopic surgery for colorectal cancer.
(a) A sigmoidectomy can be performed using three to six trocars. The laparoscopic exploration via the supraumbilical trocar (position 2) is a guide for the location of the other operating trocars. (X) The tumour location. (1) A 5 mm trocar in the left hypochondrium, for retracting the descending colon. (2) The first trocar to be introduced is a 12 mm trocar through the umbilical port. (3) A 12 mm trocar is used as an optical and operating port. (4) A 5 mm trocar is used for retracting tissue. (5) Carbon dioxide insufflation: pneumoperitoneum.
(b) The number of trocar ports for right colectomy varies from depending on the surgeon and operative difficulties. Trocar positioning is also variable, but our standard for a tumour in the caecum (shown in insert, position X) approach is to place (1) a 12 mm trocar in left hypochondrium as an optical or operating port. (2) The umbilical port side can be extended to a small laparotomy to extract the dissected colon and perform the extracorporeal anastomosis. (3) A 5 mm trocar is placed for operating and retracting the tissue (ascending colon or caecum). (4) A 5 mm trocar is used to retract the hepatic flexure, to expose ileocolic and right colic vessels, and perform the division. In both images, the patient’s head is at the top, their feet at the bottom.