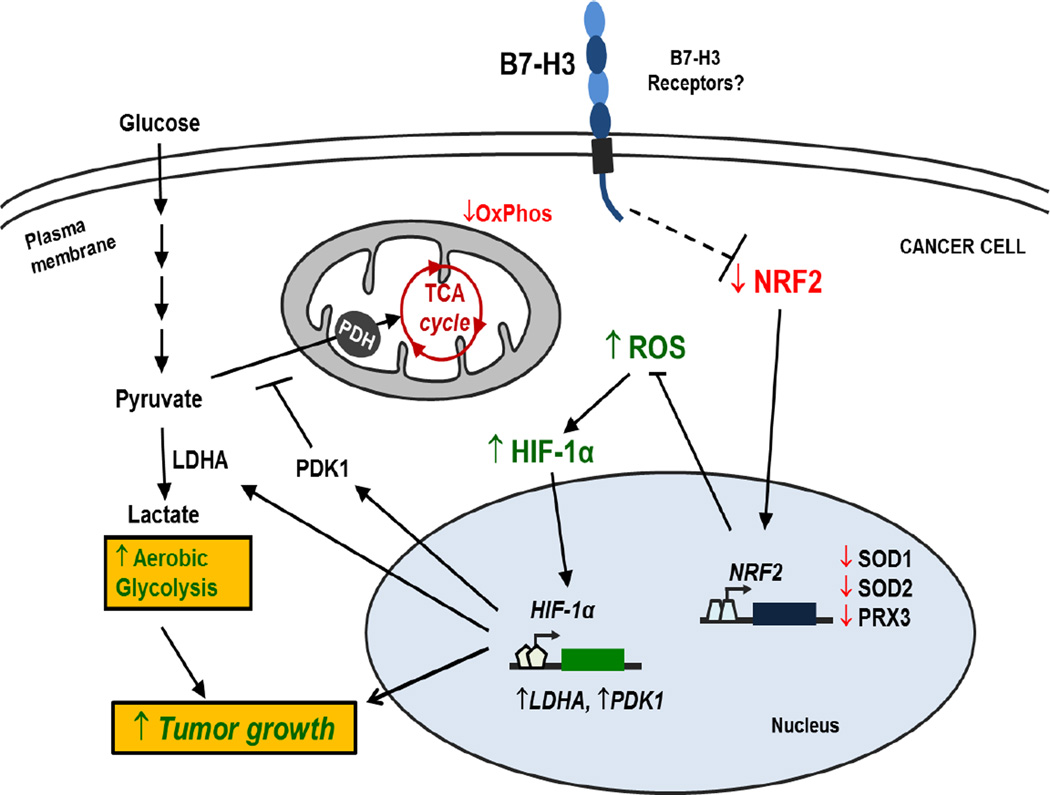
Figure 7. Model for the role of B7-H3 regulating glucose metabolism.
Through unknown mechanisms, B7-H3 suppresses Nrf2 transcriptional activity, which in turn reduces transcription of the antioxidant enzymes SOD1, SOD2 and PRX3. As a result, B7-H3 overexpression leads to increased ROS in cancer cells. B7-H3-induced ROS stabilizes HIF-1α thus increasing the expression of glycolytic enzymes LDHA and PDK1, which promotes pyruvate conversion into lactate while inhibiting pyruvate flux through the TCA cycle. As a result, B7-H3 promotes aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells and therefore tumor growth.