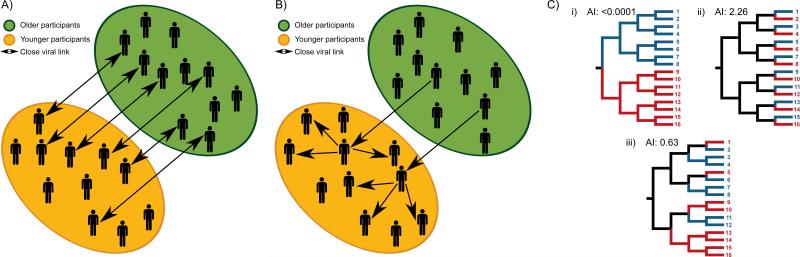
Fig 1. Potential modes of HCV transmission among people who inject drugs.
This study sought to evaluate whether: (A) HCV infection in young injectors is seeded by many transmission events between HCV-infected older injectors and younger injectors, or (B) HCV infection in young injectors is seeded by few transmission events from HCV-infected olderinjectors with further transmission among younger injectors. (C) Evaluation of phylogeny-trait correlation by Association Index (AI) illustrates the distribution of participant characteristics on the inferred phylogeny. The correlation between the phylogeny and traits may be high (i), low (ii) or moderate (iii). Permission obtained from Elsevier B.V. © Parker, J. et al. (2008) Correlating viral phenotypes with phylogeny: Accounting for phylogenetic uncertainty Infection, Genetics and Evolution doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2007.08.001