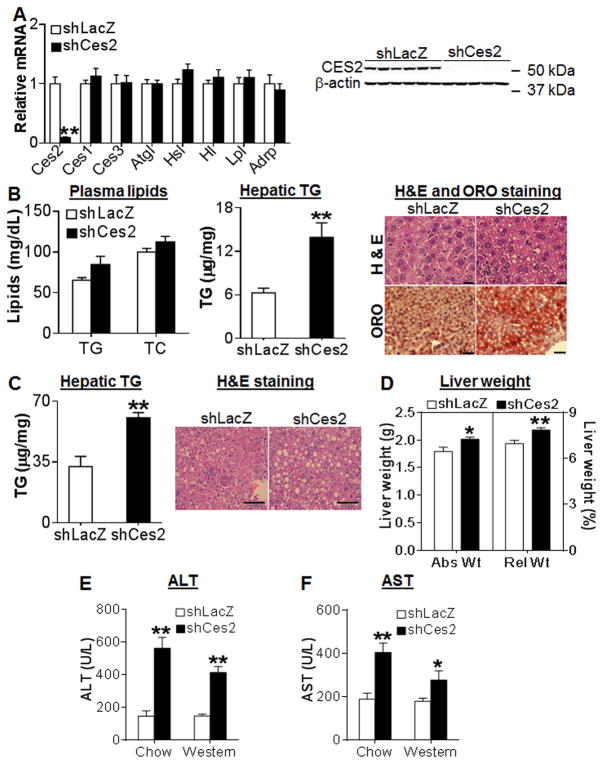
Figure 5. CES2 knockdown causes liver steatosis and liver damage in C57BL/6J mice.
(A and B) Chow-fed C57BL/6J mice were injected i.v. with Ad-shLacZ or Ad-shCes2 (n=7–8). (A) Hepatic mRNA (left panel) and protein (right panel) levels. (B) Plasma TG and cholesterol levels (left panel), hepatic TG level (middle panel) and representative H & E staining (top) or oil red O staining (bottom) of liver sections (right panel). Scale bars, 20 μm (H & E staining) or 50 μm (ORO staining). (C and D) C57BL/6J mice were fed a Western diet for 2 weeks, followed by i.v. injection of Ad-shLacZ or Ad-shCes2 (n=7–8). (C) Hepatic TG level (left panel) and representative H & E staining of liver sections (right panel). Scale bars, 100 μm. (D) Liver weight was presented as absolute liver weight (Abs Wt) and relative liver weight to whole body weight (Rel Wt; %). (E and F) Plasma ALT (E) and AST (F) levels. *P<0.05, **P<0.01