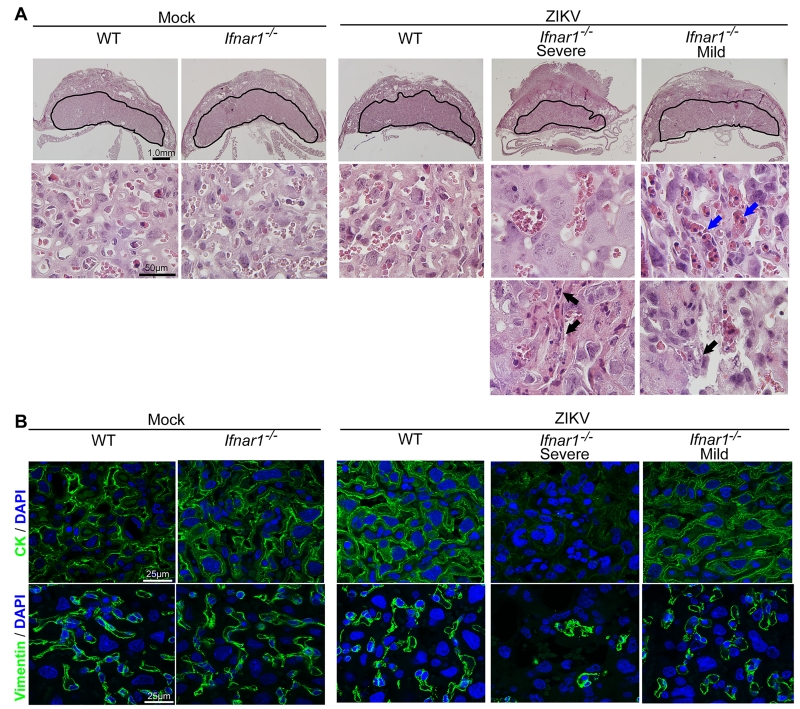
Figure 3. ZIKV infection triggers apoptosis and vascular damage in the placenta.
Pregnant dams were infected on E7.5 with 103 FFU of ZIKV via a subcutaneous route and placentas were harvested on E15.5 for histological analysis. A. Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining showed pathological features of placentas at E15.5. Labyrinth layers were marked with a solid line on the cross section of mouse placentas. Black arrows indicate apoptotic trophoblasts. Blue arrows indicate increased number of nucleated fetal erythrocytes in fetal capillaries. B. Immunofluorescence staining of cytokeratin (CK) and vimentin in mouse placentas. CK, a marker for trophoblasts; vimentin, a marker for the endothelium in fetal capillaries. See also Figure S2.