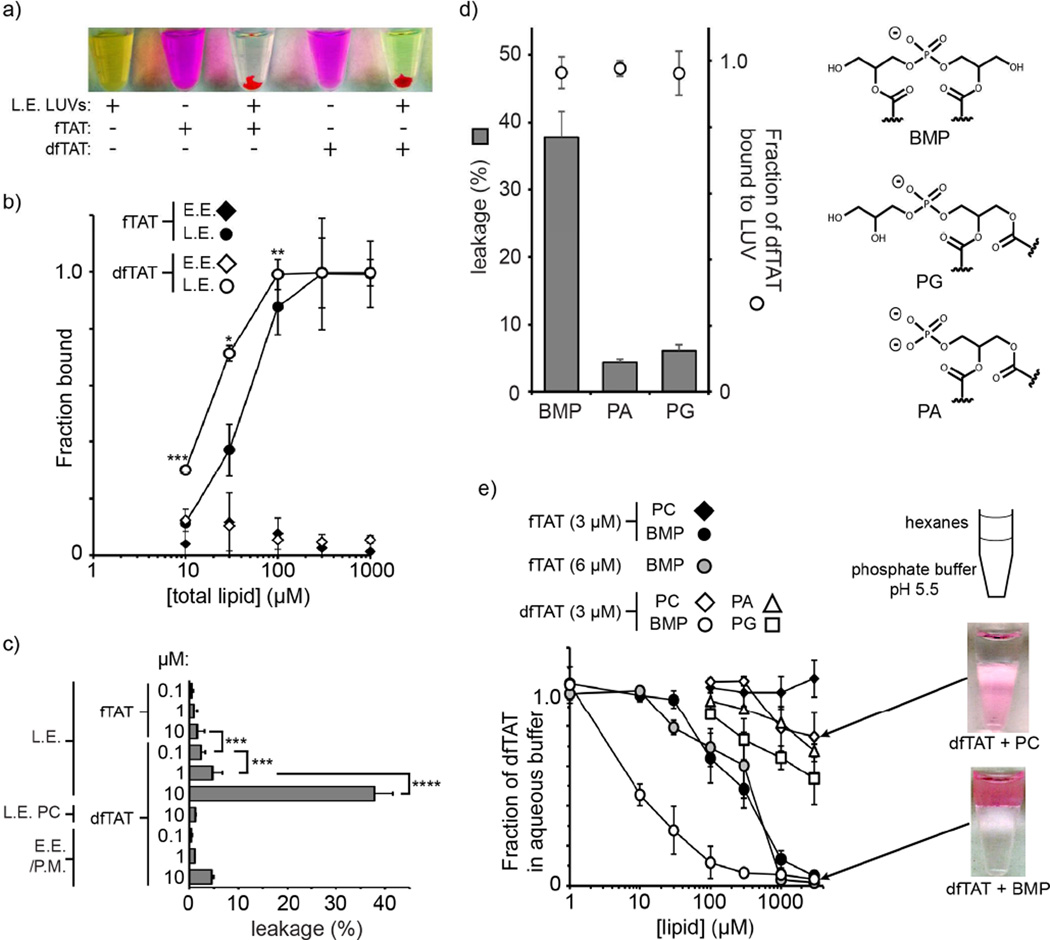
Figure 3.
dfTAT causes the leakage of liposomes of L.E. lipid composition by interacting with BMP. a) Representative images of a suspension of L.E. LUVs loaded with the green fluorophore calcein as an indicator of luminal leakage. Liposomes incubated with fTAT (10 µM) or dfTAT (10 µM) at a peptide:lipid ratio of 1:50 form aggregates containing both green and red fluorescence. The pellets obtained after low-speed centrifugation are shown. The supernatant is green (free calcein) after treatment with dfTAT but not after treatment with fTAT. P-values determined using t-test analysis are reported (*** = P≤0.001). b) Determination of the affinity of fTAT (3 μM) and dfTAT (3 μM) for multi-lamellar vesicles (MLVs) of E.E. or L.E. lipid composition. The fraction of peptide bound was determined by high-speed centrifugation of MLVs followed by quantification of the fluorescence signal remaining in the supernatant. P-values determined determined using t-test analysis between fTAT and dfTAT at 10, 30 and 100 µM are reported (*= P ≤0.05, **= P ≤0.01, ***= P≤0.001). c) Quantification of the leakage activity of fTAT and dfTAT. Liposomes of E.E/P.M. or L.E. lipid composition were incubated with peptides as shown in A. Control LUVs containing PC in place of BMP where also used (L.E. PC). The fluorescence signal of calcein was quantified and compared to that obtained upon lysis of liposomes with the detergent Triton X (100% leakage control). d) Quantification of the leakage activity of dfTAT with LUVs containing the negatively-charged phospholipids BMP, PA, PG (polar heads are represented). LUVs (77:19:4 X:PC:PE where X is PA, PG, or BMP) were incubated with dfTAT (10 μM) to a final peptide:lipid ratio of 1:50. Leakage was quantified as in c) and the fraction of dfTAT bound to LUVs was quantified by measuring the fluorescence signal of TMR from the LUVs pellet formed after low-speed centrifugation. e) BMP-mediated partitioning of dfTAT into hexanes. dfTAT (3 μM) was incubated in phosphate buffer (pH 5.5) and the lipids PC, PA, PG or BMP dissolved in hexanes at various concentrations were added. The fraction of peptide that remains in the aqueous phase upon mixing was measured by fluorescence spectroscopy.