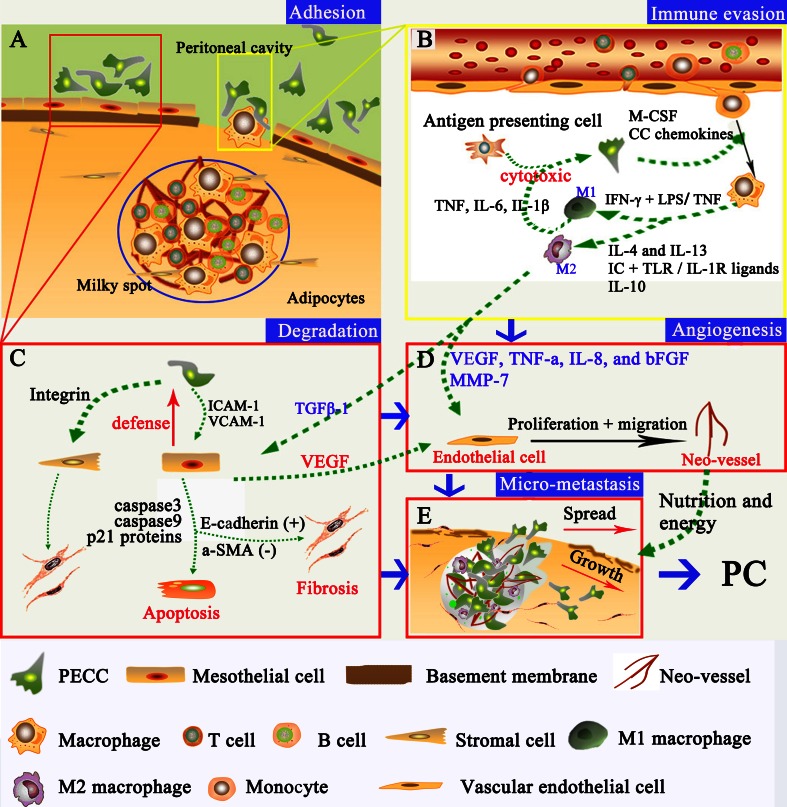
Fig. 4.
Interactions between PECC and MS cellular constituents. a Adhesion of PECC onto mesothelial cells or through the MS stomata. b Dual-functioning roles of TAMs in MS. Monocytes migrate through the blood vessels into MS region under the influence of tumor-derived chemokines and continually differentiate into TAMs, including M1 and M2 macrophages. M1 are pro-inflammatory with tumor-inhibiting effects, while M2 favor tumor growth and metastasis. c Apoptosis and fibrosis of mesothelial cells by both PECC and M2 macrophages. d Tumor angiogenesis within MS. VEGF is the most important factor to promote proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. e Formation of micro-metastasis within MS before PC occurs